Adson's sign
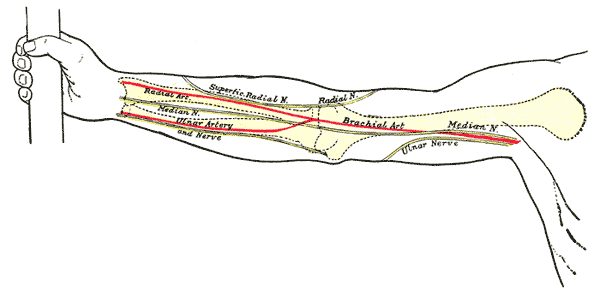
The Adson test ( also Adson maneuver, according to the U.S. neurosurgeon Alfred Washington Adson or thoracic outlet test ) is a method for the detection of certain diseases in the area of breast input ( thoracic outlet syndrome, cervical rib syndrome, Hyperabduktionssyndrom, Skalenussyndrom ).
When carrying out the patient's head is gently rotated to the limit of movement to the affected site, and at the same time the pulse is measured at the radial artery. At the turn of the head, there is a contraction of the musculi scalene muscles, through which, precisely, between musculus scalenus medius muscle and the anterior scalene ( " posterior scalene " ), the subclavian artery and the brachial plexus pass. The tension of the muscles can be increased by holding the breath in maximal inspiration, because the musculi scalene muscles belong to the auxiliary respiratory muscles.
In normal findings, the radial pulse does not change during this maneuver. In diseases in this area, however, it does a drop in the radial pulse (positive Adson test) and possibly also in neurological deficits in the upper extremity.
Original Description
- Adson AW, Coffey JR. Cervical rib: A method of anterior approach for relief of symptoms by division of the scalenus anticus. In: Ann Surg 1927; 85:839-857. PMID 17865683