Alkylpolyglycoside
Alkyl polyglycosides ( APG's ) are used as surfactants. You are nonionic surfactants and are among the sugar surfactants. Used as a surfactant component of detergents, dishwashing compositions and cleaning compositions. Alkylpolyglycosides made entirely from renewable raw sugar and fatty alcohols. They are biodegradable and have low toxicity.
History
In 1931 the first patent was filed alkyl glucosides in Germany, which discloses the use of alkyl glucosides as emulsion, detergent and wetting agent eg in soaps .. It was only in the 1970s, methods for the industrial production of APGs were developed. This eventually allowed at the end of the 1970s, the launch of the first industrially produced alkylglucoside by Rohm and Haas. The APG was an octyl / decyl polyglucoside. Nevertheless, this APG could be used only for a few purposes, as it is a not enough surfactant et al.
In the 1980s, production shifted to longer-chain alkyl groups, such as dodecyl / Tetradecylpolyglycoside. APGs were increasingly prepared for cosmetic products. The large-scale industrial production of alkylpolyglycosides was finally introduced in 1992: The Group Henkel opened a plant with an annual capacity of about 25,000 tons in Cincinnati (USA ), 1995 in Dusseldorf. Exist worldwide capacity of more than 80,000 tons per year Alkylpolyglycosides. For Germany, the annual production volume is given with 50,000 tons.
Properties
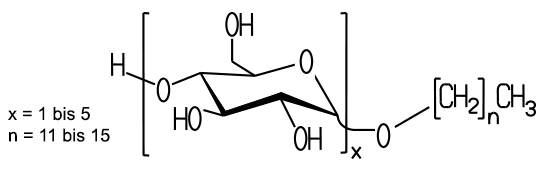
Alkyl polyglycosides are generally comprised of a sugar moiety such as glucose, and a long chain alkyl radical. The sugar component acts as a hydrophilic component, the long-chain alkyl group, the hydrophobic group in Alkylpolyglucosid dar. molecules that contain any Glucosidzucker, hot Alkylpolyglycosides. Alkylpolyglucoside contrast, compounds with glucose are called as the sugar component.
In industrial production, AGPs are present as a mixture of alkyl glucosides of different alkyl chain length, degree of polymerization of the sugar anomers and isomers. The fatty alcohols usually have a chain length of 8 to 14 carbon atoms, longer chains such as bsp. C16 lead to very hydrophobic products. The polymerization degree of the sugar is between 1 ( alkylmonoglucoside ) and 5 ( alkyl polyglucoside ).
APGs are hypoallergenic, non-toxic and readily biodegradable. In conjunction with other surfactants, they are highly synergistic, so that 20 to 50% can be saved.
Raw materials
For the preparation of alkylpolyglycosides glucose from sugar or starch producing plants is used as well as vegetable oils such as coconut or palm kernel oil as a supplier of the alkyl group.
Production
Today's production of alkylpolyglycosides based on the synthesis procedures of Emil Fischer. Here, as a starting material both glucose itself or even polymers of glucose ( starch, glucose syrup) under acid catalysis with fatty alcohols implemented (eg dodecanol ). The acid serves as a catalyst, usually sulfuric acid, p -toluenesulfonic acid, alkylbenzenesulfonic acid or sulfosuccinic acid are used. The reaction time and the course of the reaction should be well controlled, since the synthesis is stereospecific.
There are two process for preparation of AGPs. Either these are synthesized in a single step direct synthesis from glucose and eg Dodecylpoly-/Tetradecylpolyglucosid. This is done at temperatures of 120 ° C and a pressure of 2.000 Pa. The result is a complex mixture of alkyl mono-, alkyl oligo - and Alkylpolyglucosid. In addition, other by-products such as ether or glucose polymers can be detected in the reaction mixture.
Alternatively, AGPs can also be represented in two stages via a Umacetylierung, but this is more difficult in terms of apparatus. First, the reaction takes place at about 115 ° C and normal pressure with glucose and 140 ° C and 400,000 Pa, as a starting raw material starch with a short-chain alcohol, eg, butanol. In a second reaction, the short chain alkyl glucoside with a long chain alcohol, such as dodecanol, transacetalized at temperatures of 120 ° C and a pressure of from 2,000 Pa to a long-chain alkyl glucoside.
Use
Alkylpolyglycosides are resistant to hydrolysis and have, because of their HLB value of> 10 a good soil release and soil carrying capacity. They are highly exuberant and have no skin-irritating ingredients, which is why they often used in dishwashing detergents for washing dishes by hand and with linear alkyl benzene sulfonates (LAS ) and fatty alcohol sulfates (FAS ) are combined. Partly in detergents are used because of their properties as an additive.
In the cosmetics industry Alkylpolyglycosides be used as components of shampoos, hair conditioners, bath products and skin cleansers. Very hydrophobic APGs with 16 C- carbon chains are used as emulsifiers in cosmetics and foam brakemen.
The large-scale use is focused mainly on the field of cleaning agents in the food and brewing industry, where nonionic or anionic surfactants can not be used due to their poor solubility and strong foaming. Together with the modified low-foaming fatty amine ethoxylates, or even anti-foaming cleaners can be manufactured on the basis of sodium hydroxide solutions.