Ascending cholangitis
Cholangitis, also Cholangiitis, means inflammation of the bile ducts. This can be triggered by various causes, including through blockages of the bile duct by gallstones, strictures, tumors or parasites. One distinguishes the acute suppurative cholangitis, the non-suppurative destructive cholangitis and chronic sclerosing cholangitis.
Acute suppurative cholangitis
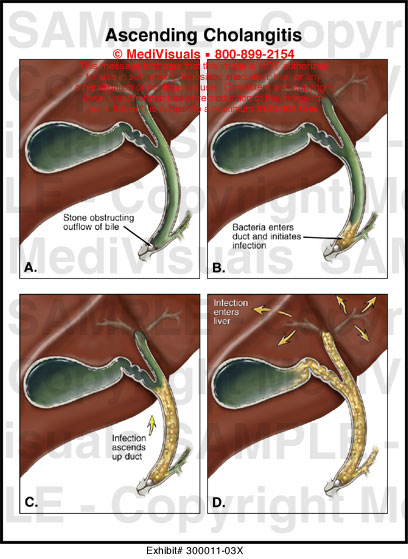
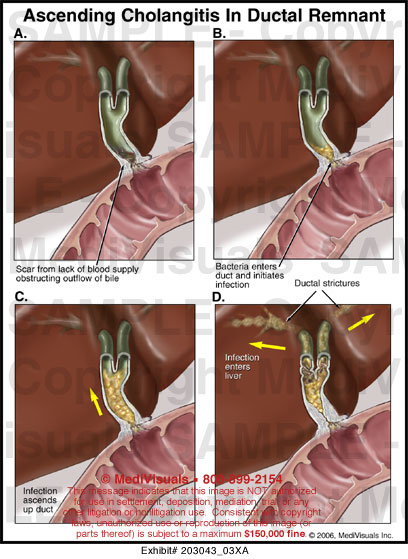
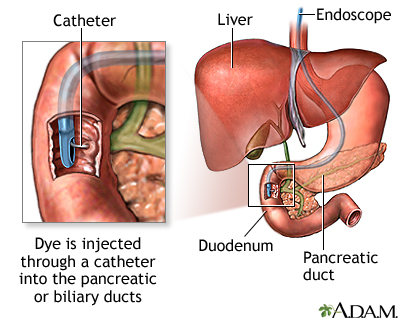
The acute cholangitis usually arises from an infection at a settlement by bacteria, usually Escherichia coli, Enterococcus and Klebsiella species, rare due to moving, mesophilic aeromonads. Occur as symptoms of a one-sided pain of the right upper abdomen, fever with chills and jaundice (icterus). The combination of these three symptoms is referred to as Charcot's triad II and is considered conclusive ( pathognomonic ) for acute cholangitis. In severe suppurative cholangitis also the reality and shock states, disorders of the central nervous system and renal dysfunction. Treatment involves endoscopic interventions at the bile ducts, such as ERCP or PTCD, restore the bile flow, and usually an antibiotic treatment.
Primary biliary cirrhosis ( PBC)
Primary biliary cirrhosis is also called non-suppurative destructive cholangitis. 95 % of those affected are women, with the peak incidence between the ages of 40 and 60 years is. Diagnosis can be found in most patients antimitochondrial antibodies (AMA -M2 ) in the blood, which is why a autoimmune etiology is assumed. The patients are clinically characterized by itching, jaundice, and hypercholesterolemia. The standard treatment is done with ursodeoxycholic acid. Later the patient can be helped only by liver transplantation.
Primary sclerosing cholangitis ( PSC)
Primary sclerosing cholangitis is a rare biliary tract disease. The cause is unknown. It was found to be associated with the antigen HLA -B8. The disease affects men twice as often as women. In 70 % of cases, can be found by laboratory diagnosis p-ANCA. Frequently it is also with inflammatory bowel diseases such as ulcerative colitis associated, for example. The standard treatment is medically performed with ursodeoxycholic acid and therapeutic ERCP ( biliary stent ). As with the destructive cholangitis, a liver transplant is also in the final stages necessary. There is an increased risk of cholangiocellular carcinomas as well as in the presence of ulcerative colitis and colon cancer.