Autonomic Computing
Autonomic computing is a paradigm since the beginning of the 21st century primarily used by the company IBM as a concept, which includes opportunities for self - configuration, optimization and healing, especially from a business perspective (and thus also cost aspects ).
Nevertheless, the approach of autonomic computing is not to be confused with the more demanding Autonomous computing or systems of artificial intelligence and robotics, and the corresponding investigation of self-organization in cognitive science.
The basic idea of autonomic computing is not new - for example, fault detection and fault tolerance are fundamental features of computer (some ) systems. Autonomy itself is actually one of the key techniques of the software architecture. The development of autonomy as the boundary between systems takes place for example in service-oriented architectures. The local interpretation of the concept of autonomy, however, is weaker, because it does not relate to self -organizing systems.
New on Autonomic Computing, therefore, the claim and the engineering-based view of self-organization as well as the application level. The latter is carried out overall view of the company, or of total and not only subsystems.
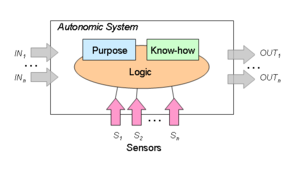
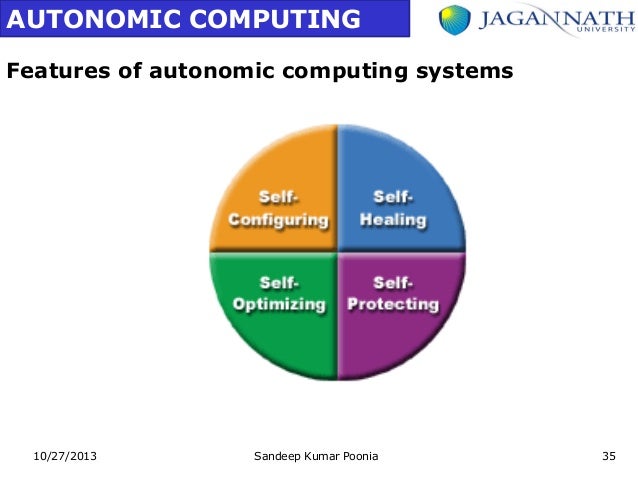
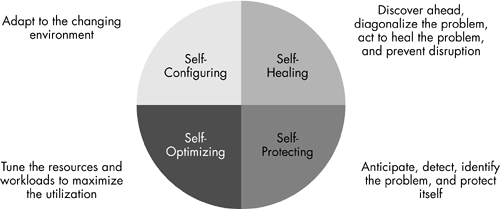
Self-management in this sense consists of four principles, which are also known as self -CHOP:
- Self -configure ( " self-configuration " ), automatic configuration of components
- Self -heal ( " self-healing " ), automatic detection and correction of faults
- Enabling self- optimize ( " self-improvement " ), automatic monitoring and control of resources to the best possible functioning with respect to the defined requirements
- Self- protect ( " self-protection " ), predictive attack detection and protection against attacks
Maturity levels of autonomy
Accordingly, five levels of maturity of a company's IT can be distinguished:
- Basic, in which the individual components of the IT infrastructure are maintained and operated separately.
- Guided where system management tools are used to centrally (s) collect the information.
- Before Saying, where with the help of analytical methods and tools possible scenarios can be calculated in advance ( " what- if ").
- Adaptive where computer systems automated actions based on information systems and extracted "knowledge" can start.
- Autonomous, is a fully -driven requirement descriptions defined goals and IT infrastructure.