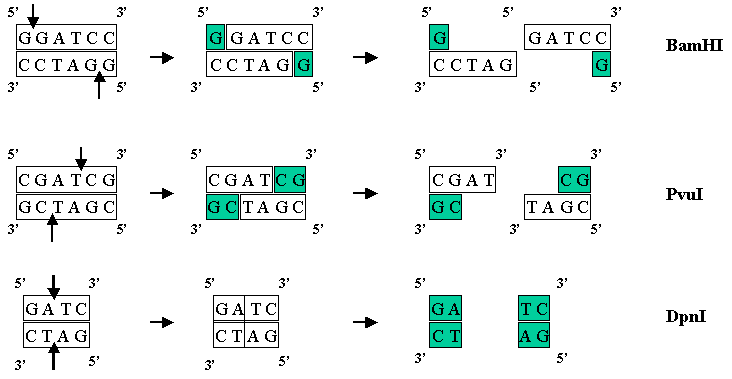BamHI
- UniProt: P23940
BamHI ( BamHI also ) is an enzyme used in molecular biology for targeted cleavage of DNA. This enzyme belongs to the family of type II restriction enzymes and was first won in 1975 from the bacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. BamHI has a molar mass of about 25 kDa. The presence of magnesium ion is essential for the enzymatic activity. After dimerization, the enzyme cuts double-stranded DNA within the palindromic recognition sequence to form a 5'- overhang as follows:
5'- GGATCC -3 ' 3'- CCTAGG -5 ' 5' -G GATCC -3 ' 3'- CCTAG G -5 ' This formation of a comprehensive four nucleic bases 5'- overhang ( sticky ends ) by BamHI is used in molecular biology with facilitated concatenation ( ligation ) of DNA fragments. BamHI is relatively heat stable and under certain conditions, shows a reduced selectivity to the recognition sequence ( star activity).