Barometer question
The Eurobarometer question ( question barometer ) is a widely used modern Sage in education and science. For the solution of a problem that actually has a recognized solution, unconventional possible solutions are offered.
Content
There are numerous variants that are identical, however, in the core:
The circulating stories and anecdotes to this question are characterized by the fact that a candidate offers a possible solution that differs from the expected response, but it is theoretically correct. In many versions of the test specimen, a wrong answer is first accused, after protests, or Impartial survey applies the question but then partially or completely answered correct. It is often argued that an examination has taken place in Copenhagen and the specimen was the young Niels Bohr been. Reliable sources to lie but not before, the oldest known sources from the 1950s.
Regardless of the debate about the possible authorship of the question and the possible responses have an important didactic side effect: They give the learners that you can also come up with unconventional solutions to aim at a clear appearing issue.
Solutions
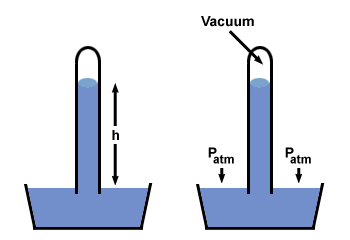
The expected response is that the specimen determined with the help of the barometer on the ground and on the roof of the skyscraper readings for the air pressure and using the barometric formula, the height of the building is calculated ( → barometric altitude measurement).
The most popular alternatives are:
- The barometer is connected to a rope and lowered from the roof of the skyscraper. As soon as the barometer touches the ground, the height of the building can be determined by measuring the rope and the barometer length.
- Description: The barometer is connected to a light rope and lowered from the roof of the building. As soon as the barometer touched the ground a little bit, it is pulled up again and swing left. With the help of the oscillation period can be the length of the pendulum and thus calculate the height of the building.
- It allows the Barometer falling from the roof of the building and stops the duration of the fall with a stopwatch. The case length and thus the height of the building are determined by using the formula for the free fall.
- It examines how many " barometer units " (length of the barometer ), the building is high, for example by reacting the stairs with the help of markers move piece by piece the barometer and then calculates the " barometer units " into the desired length around.
- In sunny weather you can set up the barometer and measure the height of the barometer and the length of its shadow. Then we determine the length of the building shadow and calculated from a ratio equation, the height of the building.
- With a shorter rope letting the barometer as a pendant on the ground first, then swing on the roof of the building and measures each period of oscillation. From these values we calculated the difference in gravitational acceleration and the difference leads to the building height (→ gravimetry).
- The barometer is thrown from the roof into a water tank. From the temperature difference you can Kinetic energy, the drop height (ie the height of the building ) calculated.
- You throw the barometer from the roof of the building and determined the kinetic energy from the deformation of the barometer.
Complicated:
- For Barometer with Brass Housing: Man raises the barometer from the roof of the building by the pole pieces of a permanent magnet lying on the ground and determines the Hall voltage at two lateral, opposite points of the barometer housing. From this voltage, the speed of the barometer may directly before impact and from this the height of the building can be calculated with the laws of falling bodies.
- The barometer by means of a rocker and a weight to speed vertically upward into the air so that the dead point at the height of 20 barometer lengths. Support the needed weight will be recorded. In the next experiment, the same is made; this time the dead point at the height of the gable roof should be. Using the factor of the required weight gain multiplying the " 20s barometer height" and thus comes to the " barometer height" of the entire house. This is converted into a desired measure. To confirm the amount then, one can measure the actual flying time and using the formula for calculating the height of free fall, so far as one still involves the acceleration time in the rocker. Thus, one can still prove triple the whole, the deformation of the barometer by means of kinetic energy in the height of the building will be converted, as the barometer also still falling.
What is noticeable in these responses that the expected by the examiner measurements with the barometer (air pressure ) with other measurements (time, length, temperature or voltage ) can be replaced, so it would theoretically be additional aids required to determine the height of the building. If no specific measure of length would be specified, one could for the measurement of the rope or the shadow (see above) also use the aforementioned barometer units.
In addition, circulating more solutions that do not require measurements. These responses are not based on physical or mathematical laws:
- We visited the caretaker of the building and gives him the barometer, after betraying a building height.
- The barometer is used as weight when ( wherever) looks through the blueprints of the building.
- It enables the building by striking with the barometer resonated until it collapses - the next day in the newspaper, how high it was.
- It leaves the barometer as collateral to obtain a laser differential knife with which to measure the height of the building. Thereafter, the barometer can be triggered upon return of the altimeter again.