BASF Plant Science
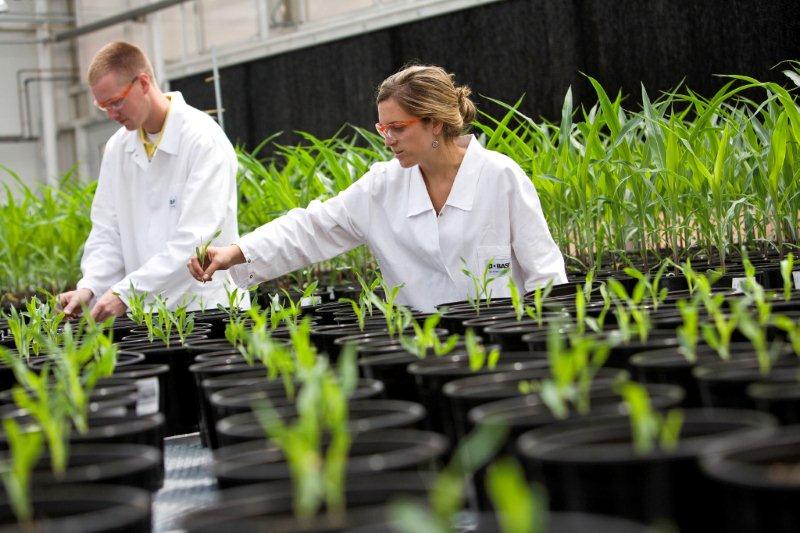
BASF Plant Science is the plant technology company BASF. It is headquartered in the BASF Agricultural Center Limburgerhof and in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, and is working on her research locations in the development of genetically modified seeds in order to increase the efficiency of plant and expand the possibilities of the use of plants as a renewable resource.
Company Profile
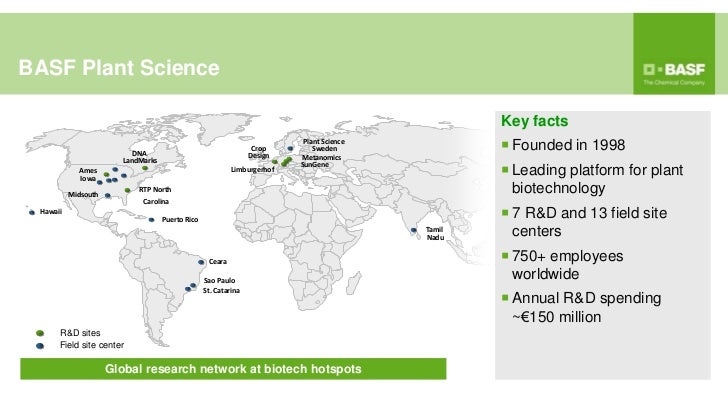
BASF Plant Science GmbH was founded in 1998 and currently employs approximately 700 employees spread over 8 locations worldwide.
The company is working on the genetic optimization of plants ( corn, soy, cotton, canola, sugar cane, sugar beet, wheat and potatoes) for more efficient agriculture through more agricultural yields of crops, healthier nutrition through higher nutrient content, and the use of plants as renewable raw materials.
Together with its subsidiaries and affiliates, as well as in collaborations with universities and research institutes, BASF Plant Science develops new methods and applications.
Through partnerships, such as Monsanto, KWS, EMBRAPA, or CTC (Centro de Tecnologia Canavieira ) developed seed varieties are sold.
In January 2012, BASF Plant Science relocating your corporate headquarters in the United States and the research activities of Limburgerhof to North America, Ghent and Berlin decided. Along was based on a lack of acceptance in Europe, the setting of the research activities for products that are designed exclusively for the European market announced. Ongoing approval process will be continued.
Products
Two developed by BASF Plant Science Products, Cultivance and NutriDense be sold by local growers.
- Cultivance: It is a resistant to herbicides soybean variety. This 2010 received marketing approval for Brazil. The marketing takes EMBRAPA.
- NutriDense: A cultivated fodder maize, which is characterized by an increased forage nutritional value for pigs, chickens and cattle and allows less feed the same amount of production of milk, meat and eggs to obtain.
- Amflora: Is designed as a renewable resource potato for the European market. The containing amylopectin in potato starch will dissolve out after its been used in industry to make paper glossy, yarn tear-resistant adhesive or adhesive.
A number of other crop seed is in the development pipeline:
- Corn, soybeans, canola, cotton: Target is a higher crop yield for farmers around the acreage by more crops and plants that better withstand drought periods and thereby provide less crop failures. The development and marketing is done in cooperation with Monsanto. The adopted 2007 Cooperation includes a research budget of up to $ 1.5 billion. 2010, the portfolio was expanded to include wheat and additional up to a billion dollars.
- Sugar cane / sugar beet: the objective is the development of seed which at the Growing of sugar per production area provides, which can be then used as food and / or for the production of bioethanol.
- Potato: Under the name of Fortuna, a potato is developed, which is resistant to the disease late blight, a potato disease that is self- control nowadays for European farmers, despite consuming plant protection measures barely. In November 2011, BASF Plant Science requested the approval of Fortuna potato as food. Application is to find these type of potato than french fries and potato chips potato.
- In addition to the commercially grown potato Amflora BASF Plant Science applied in August 2010 for European approval for a further amylopectin potato cultivar name Amadea. The strength of the potato should be used in addition to the industrial sector in the food industry. The market launch is planned for 2013/2014.