Canonical XML
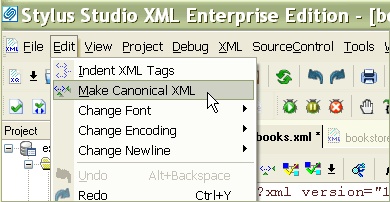
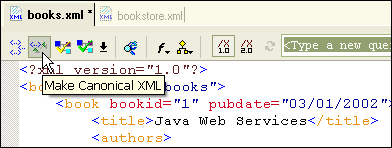
Canonical XML called the canonical form of XML documents, which is to facilitate the comparability of two such documents. For this reason, removes the Canonical XML transformation insignificant differences between the documents. Each XML document can be brought into the canonical form ( Canonical XML).
For example, XML allows the occurrence of spaces at certain points within the start - tags, and attributes can be specified in any order. Such differences are, if at all very rarely provided, with a meaning. For this reason, the following two forms are generally regarded as equivalent:
Due to the conversion of any XML document in canonical XML attributes its nominative order to be sorted ( alphabetically by their name ) and the spaces and quotation marks are unified. Thus, the second form will be converted into the first form.
Canonical XML specifies a number of other details, some of which are listed here:
- The UTF -8 character encoding is used
- Line endings are by the character 0x0A ( New Line = line feed) represents
- Spaces within the attribute values are standardized
- Entity references are expanded
- As a CDATA marked sections are not used
- Empty elements are encoded as start and end pairs, not by using the syntax for empty elements
- Default attributes are explicitly marked as such
- Superfluous namespace declarations are deleted.
To convert a document to Canonical XML, is idempotent. This means that change in the first conversion, the characters than the original shown, shall be carried out in further transformations any further changes.
According to the W3C, two documents within the given application context as logically equivalent to be considered, if they have the same canonical form (except limitations in terms of some rarely occurring cases).
However, users could put in special environments value to specific semantics, which are outside the general logical equality is associated with the Canonical XML. For example, a steganographic system in an XML document by changing spaces, quotation marks and arrangement of these attributes, the use of hexadecimal vs. decimal character references, etc. hide information. Obviously go lost these special semantics by converting such a file in Canonical XML. However, even XML files that are in the use of upper - vs. Sensitive, no or those old vs. use new spelling, etc., are considered equivalent for certain purposes. Such contexts are outside the scope of Canonical XML.
Software
An implementation of Canonical XML is to be found in the program xmllint, which is part of gnome libxml2 and next to it is available for Microsoft Windows.
Example application:
Xmllint - C14N SomeXml.xml > CanonicalVersionOf_SomeXml.xml see also
- XML Signature