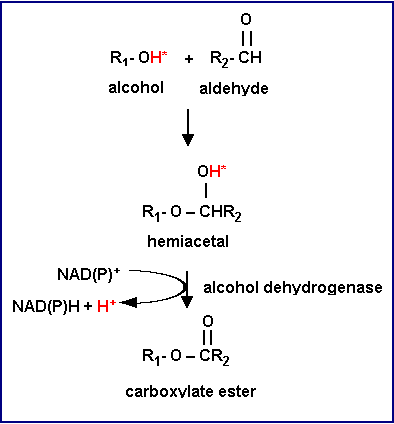
Carboxylate ester
Carboxylic acid esters (R1 -CO-O -R2) are esters that are formally from a carboxylic acid ( R1 -CO- OH) and an alcohol or phenol ( R 2 -OH) are composed. Esters of short-chain monocarboxylic acids are as fragrant compounds in essential oils ( sogn. fruit esters) and those of longer-chain monocarboxylic acids in natural waxes.
Vegetable and animal fats and oils are triple esters (triglycerides ) of the fatty acids and the trivalent alcohol glycerol. Many polyester polymers are carboxylic acid esters of the dicarboxylic acids and diols and have a plastics importance. The carboxylic ester is ethyl acetate, a commonly used solvent.
Nomenclature and structure declaration
Carboxylic acid esters are composed of a carboxylic acid moiety and an alcohol moiety. In trivial names of the carboxylic acid ester of the name is often composed of the names of the carboxylic acid and the term for the organic moiety of the alcohol, and from the word acetate. An example is ethyl acetate, whose name is formed from acetic acid, the alkyl group of the alcohol ethanol ( ethyl ) and the word esters.
However, the systematic name of this ester is Ethylethanoat and is based on the " rest of the alcohol ( = ethyl ) base of the acid ( = ethane ) oat" formed. However, the suffix "R- oat" is not allowed for all connections. Is located in a connection, a further functional group with a higher priority, such as an acid or a cation, then the ester must be referred to as a prefix. The name to be used is R- oxycarbonyl.
Examples
Physical Properties
Due to the electronegativity difference between carbon and oxygen, the carboxylic acid ester group is polar and allows, in principle, a solubility in water through the formation of hydrogen bonds. From the short-chain carboxylic acid esters methyl acetate is about 250 g / l dissolved in water. From the slightly longer chain acetate only go about 10 g / l in solution. The overall solubility is determined by the organic radicals, so that at sufficiently non-polar residues, the solubility in water becomes very low. Most of the esters are hydrophobic and are oils or waxes.
The boiling points of the short-chain carboxylic acid esters are in comparison to alcohols or carboxylic acids of a comparable molar mass substantially lower, since they can otherwise as carboxylic acids or alcohols, do not form strong hydrogen bonds.
Reactions
Synthesis
Alcohols and carboxylic acids can be converted to carboxylic acid esters by esterification. The esterification is carried out by an acid as a catalyst and is an equilibrium reaction. By removal of the resulting water from the reaction mixture, for example by azeotropic distillation or by use of a molecular sieve, the equilibrium is shifted towards esters.
In addition to the reaction of carboxylic acids, reactions of the corresponding carboxylic acid and carboxylic acid chlorides lead to esters. Another industrially important reaction is the transesterification of the alcohol in the ester exchange one with another. This is used for example to produce the methyl ester of rapeseed oil, the fatty acids can be used as biodiesel.
Ester cleavage
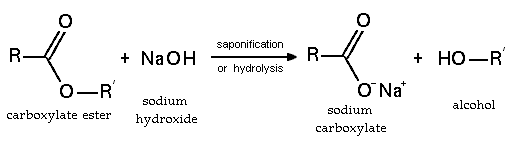
Esters can be cleaved hydrolytically and pyrolytic. Most bases are also used acids for the hydrolysis. Upon cleavage with acids are formed according to the starting material used, the alcohol and the carboxylic acid. If the esters with bases split, incurred by the respective alcohol and the carboxylate anion. Since in the latter lack the necessary for the reverse reaction, acidic hydrogen atom, this reaction is irreversible, i.e., non- reversible. This makes it possible with an excess of one reactant, such as the alcohol, to carry out a quantitative (ie full ) due to ester hydrolysis according to the principle of least constraint Henry Le Chatelier. The basic ester cleavage is called saponification.
By saponification of fats and fatty oils, the alkali metal salts of fatty acids, ie, the soaps, won. The ester cleavage can also lipases, a group of enzymes take place, which play an important role in the digestion of fats. Has practical significance for the ester cleavage in detergents containing lipases to split the water-insoluble grease residues on fabrics to form tolerably water-soluble fatty acids and highly water-soluble glycerol. To obtain enantiomerically pure carboxylic acids or alcohols enantiomer racemic carboxylic acid ester is stereoselectively cleaved in chemistry. Here, the second enantiomer of the carboxylic acid ester remains unchanged and permits the racemate separation.
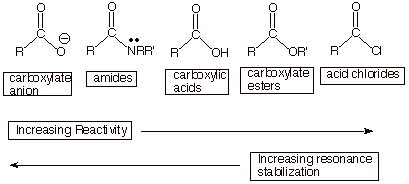
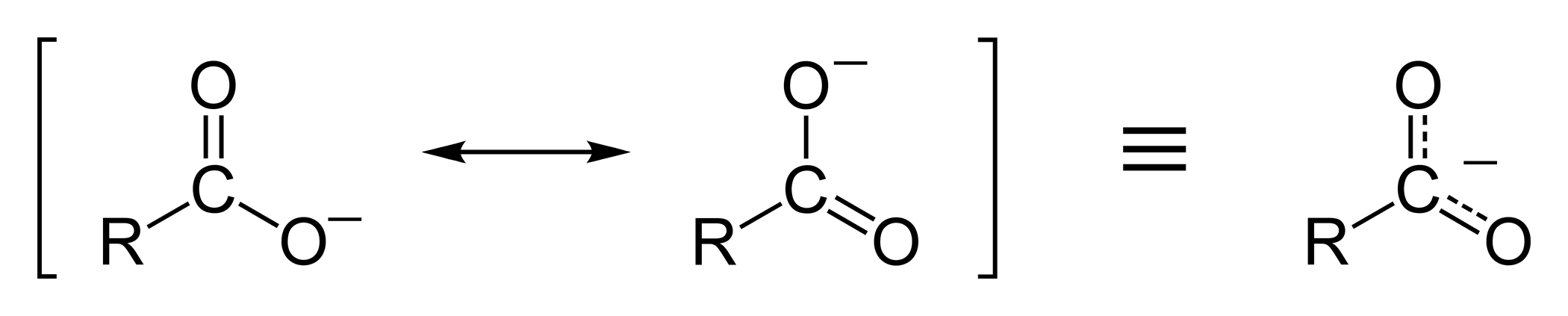
C, H acidity
Esters are not acids but C, H -acidic compounds, since the proton in α - position cleaved by very strong bases ( abstracts ) can be. This creates a resonance-stabilized enolate:
Acid moiety versus the alcohol moiety
As shown, originates in the (often normal ) form the ester of carboxylic acid and alcohol of the blue curve portion of the ester from the alcohol (in this case ethanol) and the part shown in red from the carboxylic acid ( here: acetic acid). An exception is the formation of esters of the carboxylic acid salts ( carboxylates ), and alkylating agents; Here comes the blue shown in the picture oxygen from the carboxylic acid.
In the cleavage of esters ( both acidic basic katalysierbar ) of the alcohol thus formed contains the oxygen shown in blue in the image. Again, there is one exception, namely the acid-catalyzed cleavage of esters of tertiary alcohols in which the alcohol part of an alkene is formed (E1 reaction).
The fact that the remaining oxygen atom in the ester formation comes from the alcohol, it can be demonstrated by isotopic labeling using the oxygen isotope 18O.
Further reactions
- Aryl esters can react to aryl ketones by Fries rearrangement.
- Specific esters could enter into a Chan rearrangement.
Carboxylic acid esters deposits in fruit ( selection)
Apples contain 2 Methylbuttersäureethylester, butyrate, acetic acid -2- methylbutyl ester, acetic acid n-butyl undEssigsäurehexylester.
Bananas contain amyl acetate, butyric acid -3- methylbutyl, 3 -methylbutyric acid 3- methylbutyl ester
Pear include amyl acetate, (2E, 4Z ) - deca- 2 ,4- dienoic acid ethyl ester
Strawberries contain methyl anthranilate, ethyl butyrate, hexanoic acid ethyl ester
Kiwi contains 3- hydroxybutyrate
Tangerines contain N- Methylanthranilsäuremethylester
Contains passion fruit butyrate, hexanoic acid ethyl ester, Buttersäurehexylester, Hexansäurehexylester
Peaches contain esters of acetic acid
Plums contain cinnamic acid methyl ester
Quinces contain 2- Methylbuttersäureethylester