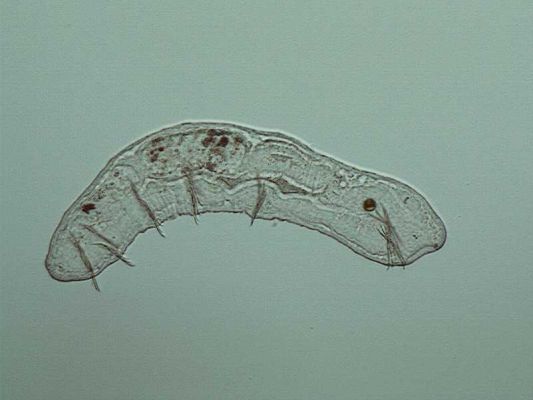
Chaetogaster
The genus Chaetogaster ( German " Bauchborstenwürmchen " ) is one of the segmented worms ( Annelida ). It is provided to the family of Naididae from the order of Little Borster ( Oligochaeta ); within the Naididae it belongs to the subfamily of Naidinae. It is about 2-25 mm long transparent aquatic living worms that partly as a result of asexual reproduction form conspicuous animal chains and occur frequently in fresh water.
Morphology
Externally, the animals comply with the general plan of Naidinae, however, have in contrast to the other species their setae ( bristles) only on the ventral side ( hence the name). The size of the animals and also the setae is quite variable, even within individual species.
Occurrence and diet
Although the animals are mainly used in standing or flowing fresh water before, but lives the largest species, Chaetogaster diaphanus, also in brackish water. All species appear to be very widely used in Europe and are, moreover, often seen on many continents.
The animals generally act usually quite lively, but can not specifically swimming. Therefore, you live on solid ground ( on plants or rocks, a subspecies on snails). They feed by sucking in small organisms of suitable size. The food composition differs between species because the different body size also leads to different soaked food components. While the largest species Ch diaphanus organisms in the order of about 0.3 to 3 mm long consumed, which usually represent small animals ( rotifers, cladocerans, etc.), preferably about Ch limnaei organisms in the order of about 0.03 to 0, 3 mm, which are mainly algae (diatoms and green algae ) or very small animal organisms. Basically, the species are thus omnivorous, but which take up most of the vast majority of animal food, the smaller particles tend to be quite herbal. How unselective the food is taken is also evident that repeatedly sand or any other virtually indigestible particles (eg Coniferenpollen ) are found in the stomach, which are also located in the specified size range.
Physiologically are Chaetogaster species has long been known that they show similar to the vertebrate an acidic stomach reaction.
The special case of Chaetogaster limnaei
A special feature is the type Ch limnaei, which occurs in two " subspecies ", which differ markedly in their lifestyle. One subspecies feeds parasitically in the interior of snails ( Ch l vaughini ) and affects only snails from a certain minimum size. It feeds mainly apparently of kidney cells of the host snail. The other subspecies (C. l limnaei ) attaches itself firmly to the outside of the worm (eg the genera Lymnaea, Physa, Ancylus or Orbis Australasia ) on the soft body and on the inside of the shell where it can change freely (so-called Epökie ). They consumed various small organisms that they can catch from their host by ingestion, except where, for example, Rotifers and algae also Cerkarien and miracidia ( larvae of trematodes ) are among their food. On several of the ecological context, this all but biological control of parasites was investigated. He seems to be less pronounced, but can obviously not practical to apply. Sometimes the subspecies Ch l is limnaei found on freshwater mussels, and in particular of the genus Sphaerium.
Reproduction
Like virtually all representatives of Naidinae distinguished the species of the genus Chaeogaster by many asexual reproduction from. Characteristic is the formation of two or more animals in the form of animal chains, resulting in a kind of budding. By dividing ( paratomy ) this animal chains new individuals can access asexually arise, which are genetically identical copy of the parent animal. However, it comes in between (especially in late summer / autumn) in many cases to normal bisexual reproduction. The subspecies Ch l limnaei leaves it in the late summer / autumn of their host ( the snail ) will go to the free life in the waters over and attacks in the spring of new worm individuals.
System
Belonging to the genus Chaetogaster to the family Tubificidae and to the subfamily of Naidinae is meanwhile out on morphological and molecular genetic findings about as secure. The closest relationship seems according to cytochrome oxidase I - to insist sequence studies on the genus Amphichaeta (see Naidinae ).
The genus Chaetogaster Baer 1827 is currently (ie valid nomenclatural ) divided into nine types valid:
- Chaetogaster cristal linus Vejdovsky 1883, sometimes also written as Chaetogaster crystal linus Vejdovsky 1883; Animal long chains to about 7 mm; frequently.
- Chaetogaster diaphanus ( Gruithuisen 1828); usually 10-15 mm long, in the extreme case of 2.5 mm ( small individual animals) to 25 mm (large chain animals) long; frequently.
- Chaetogaster diastrophus ( Gruithuisen 1828); frequently.
- Chaetogaster diversisetosus Sporka 1983; occasionally.
- Chaetogaster krasnopolskiae Lastockin 1937; occasionally.
- Chaetogaster langi Bretscher 1896; widespread.
- Chaetogaster limnaei Baer 1827; disseminated; consisting of two distinct sub-species with different habitat: Ch l limnaei Baer, 1827 and Ch l vaghini Gruffydd in 1965 (for details see above).
- Chaetogaster parvus Pointner 1914; widespread.
- Chaetogaster setosus Svetlov 1925; widespread.