Chédiak–Higashi syndrome
The Chediak -Higashi syndrome ( CHS) is a very rare genetic disease that is increasingly observed in Jewish populations.
Diagnosis
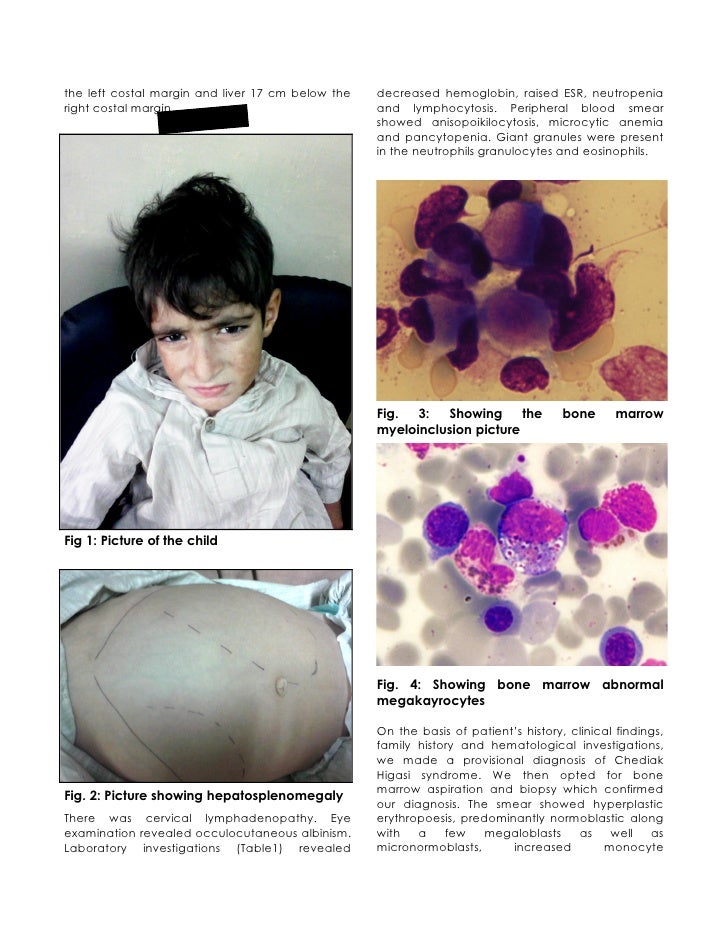
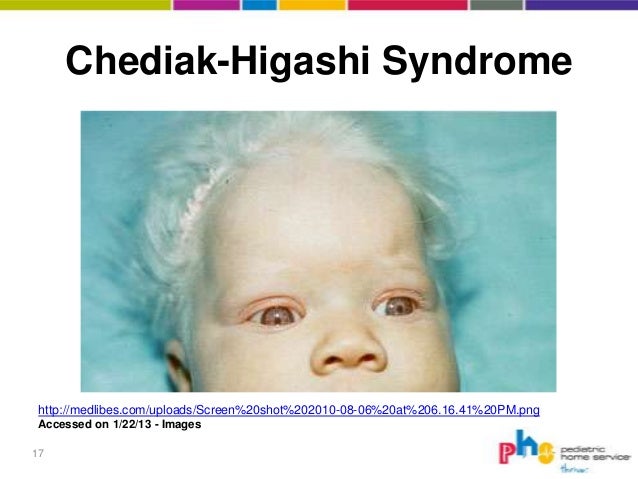
The Chediak- Higashi syndrome manifests with oculo - cutaneous albinism ( decreased pigmentation ), silvery- blond hair, hepatosplenomegaly, ganglion hypertrophy and recurrent purulent infections of the skin and the respiratory tract.
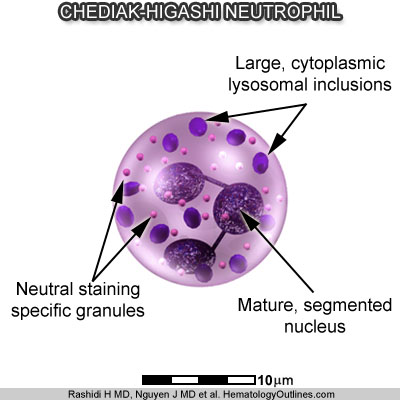
In the peripheral blood leukocytes and lymphocytes of a Granulationsanomalie ( giant granules ) and plasmatic inclusion is visible in the myeloid cells in the bone marrow. In prenatal diagnosis, the disease can be detected by fetal blood test or a skin - hair - biopsy.
Cause
The syndrome is inherited as an autosomal recessive trait. The CHS gene located on the long arm of chromosome 1, locus q42.1 - q42.2. Causes of the symptoms are functional disorders of polymorphonuclear leukocytes ( they contain characteristic large lysosomal vacuoles ) and a lack of natural killer (NK ) lymphocytes. The investigation of an animal model, the beige mouse, led to the discovery of the cause, mutations in the gene for the LYST protein whose function is not yet known.
The Chediak -Higashi syndrome is a aggressive running Periodontal disease is usually associated.
Therapy
The disease can be treated by bone marrow transplantation.
Forecast
The life expectancy is greatly reduced. Most suffering from CHS children do not reach the second decade of life as a result of infection or due to the formation of malignant tumors.