Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate
- Boc- anhydride
- DIBOC
- Boc2O
- Di -tert- butyl pyrocarbonate
- Pyrokohlensäuredi tert-butyl ester
Colorless solid or liquid
Liquid
1.02 g · cm -3 ( 20 ° C)
20-23 ° C.
56-57 ° C ( 0.7 hPa)
Insoluble in water
Risk
Template: Infobox chemical / molecular formula search available
Di -tert- butyl dicarbonate ( commonly known in the laboratory - but erroneously - usually Boc anhydride ( Boc2O ) and DIBOC called ), is a liquid chemical compound which may structurally be expected both to the esters and the anhydrides.
Use
The main use of di-tert- butyl dicarbonate, the introduction of the tert -butyloxycarbonyl group ( Boc group ), one of the most commonly used protecting groups in organic chemistry. It is the most widely used chemical for protection of amino functions in chemical reactions, particularly in peptide and Glycopeptidchemie.
Production
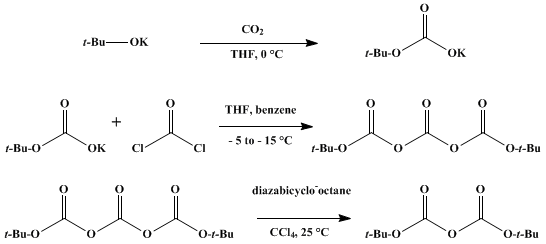
Di -tert- butyl dicarbonate is produced worldwide by two methods: on the one hand, by the reaction of sodium or potassium tert- butoxide, with phosgene or phosgene derivatives and on the other hand, the catalytic reaction of sodium tert- butoxide with carbon dioxide. The representation of potassium tert-butoxide and phosgene proceeds according to the following scheme:
Cleavage
Boc protecting group can - in contrast to the Cbz protecting group - already by means of dilute aqueous acid ( ≈ 3 M HCl) via SN1 step are eliminated. The cleavage products are CO2 and isobutene, both are volatile and thus do not contaminate the deprotected amine. Boc is extremely stable to bases and even compared with OH, as the carbonyl group is sterically hindered.
The mechanism of cleavage: