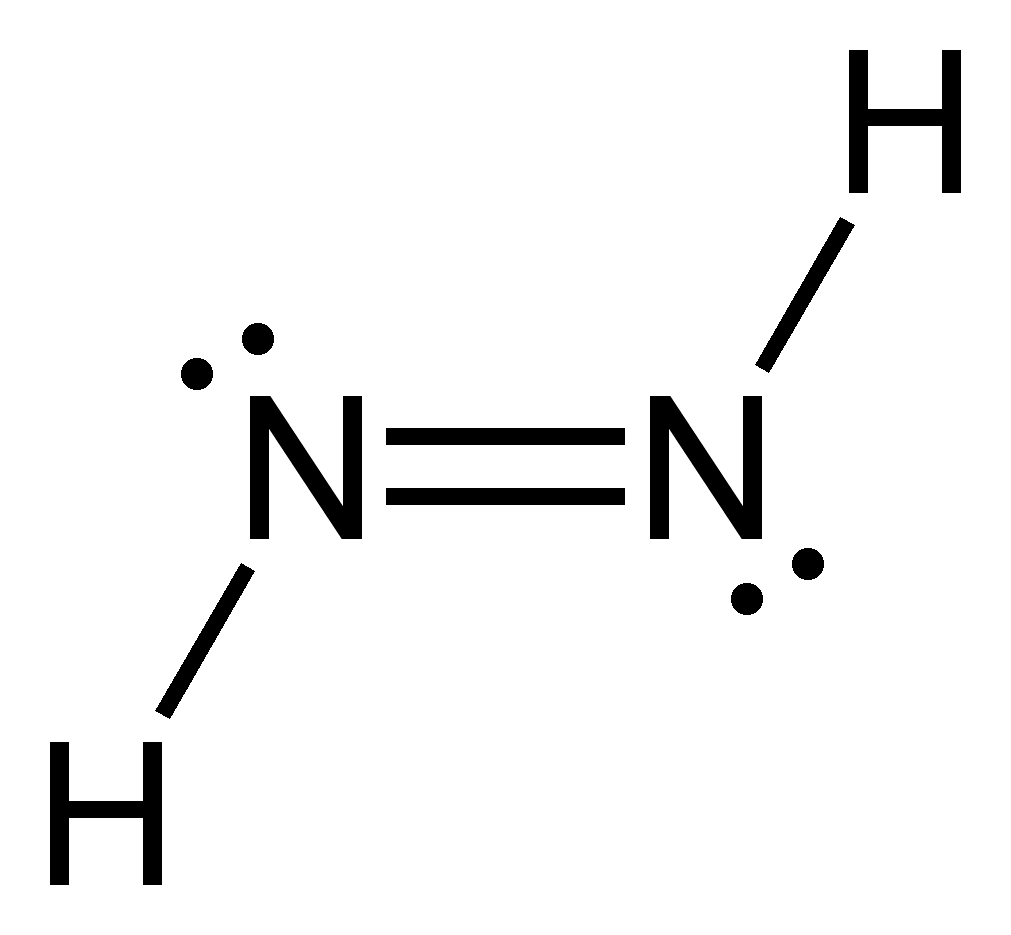
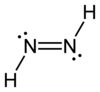
Diazene
- Diazene
- Diimide
- Azowasserstoff
Bright yellow, metastable solid below -180 ° C
Template: Infobox chemical / molecular formula search available
Diimine (also diazene, diimide Azowasserstoff ) is an inorganic compound, forming the basic structure of the organic azo compounds. It is unstable at room temperature. Pure, solid, metastable below -180 ° C diimine has a bright yellow color. The connection is not sublimed without decomposition, very light sensitive and decomposes to disproportionation into nitrogen and hydrazine.
Production and representation
Diimine can be obtained in the following ways:
- By the dehydrogenation of hydrazine ( for example, by exposure to microwaves)
- By conversion of azo compounds ( for example, by protonolysis of Azodicarbonat )
- By hydrogenation of nitrogen
Isomerism
History
The substance was isolated in 1972 by Nils Wiberg and co-workers for the first time. Here, a thermolysis of Natriumtosylhydrazid was carried out under vacuum at 60 ° C. The tosylhydrazide disintegrated while with 80 % yield in diimine and sodium toluenesulfinate. The diimine was deposited as a bright yellow coating at -196 ° C in a cold finger. The detection was carried out in the gas mass spectrometry. The production succeeded with other Alkalimetalltosylhydraziden, albeit in lower yield.
Diazenes, triazenes, tetrazenes
From diimine guided formally from the diazenes in which the hydrogen atoms of the diimine are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. However, they are commonly referred to as azo compounds. Diazenes in principle, in a (E) - or (Z ) present form, of which the former is the energetically more favorable (see cis- trans isomerism ).
Formally, let the triazenes and tetrazenes derived from the diimine. A stable derivative of triazene is for example the diazoaminobenzene. A Tetrazenderivat obtained by oxidation of phenylhydrazine in the form of yellow 1,1,4,4 -tetraphenyl -2- tetrazene.
Diazenyl residual
In the IUPAC nomenclature, an azo bridge are called Diazenyl radical.
Inorganic derivatives
A derivative of the diimine is the Hyposalpetrige acid ( Diazendiol ). Another derivative is the Difluordiimin N2F2 ( Difluordiazin ). Also include the Azosäuren ( Diazendicarbonsäure ) or its stable amides and esters ( for example, diethyl azodicarboxylate ) on derivatives. In addition, Azosilane how the trans-bis ( trimethylsilyl ) diimine known:
Diimine complexes
Are known, for example, polynuclear carbonyl complexes with chromium, and cyclopentadienyl complexes of manganese, which can be prepared by oxidation from the corresponding hydrazine complexes. In contrast to pure diimine this diimine complexes are relatively stable in the solid state, in solutions but also highly reactive.