Education in Spain
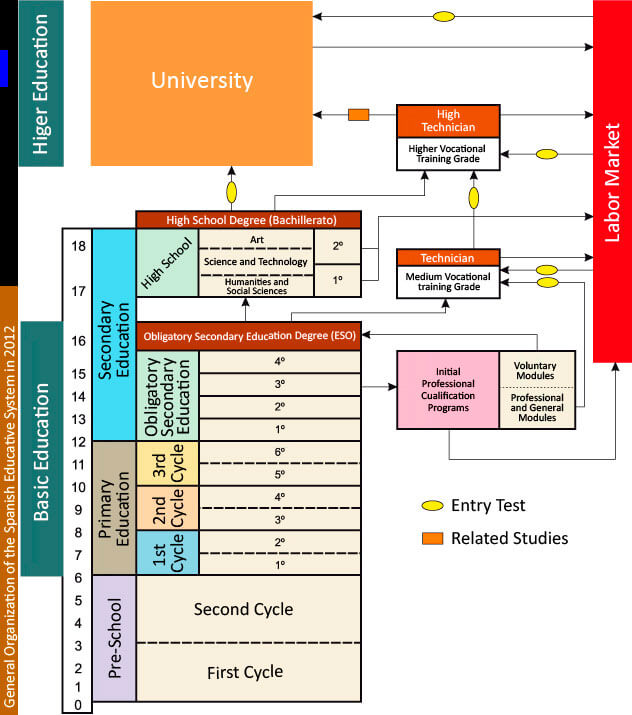
The school system in Spain is divided into three blocks. The Educación Primaria lasts six years, the second block with the Educación Secundaria Obligatoria ( ESO) lasts four years. These include Spanish students mostly from the age of 16. Education is compulsory up to the age of 16 years.
The school system in Spain is different from the education system in Germany in many respects.
The currently applicable in Spain Law on the Regulation of the education system " Ley Orgánica de del Sistema Educativo Ordenación - LOGSE " dates from 1990, it forms the basis for the dichotomy between public and private educational institutions and regulates the participation of the institutes. . Politically spread the responsibility for education, as in Germany, to the central government - in this case the Ministry of Education, Culture and Sport is responsible - and the respective Autonomous Communities in Spain.
According to the Spanish law, there is a ten-year, compulsory education for ages 6 to 16 years. Despite the free public schools around thirty percent of children attend private school, usually a Catholic institution. In the Spanish school system, which heavily based on the French model, is a general upper secondary education leading to the " Bachillerato ", equivalent to the German Abitur, are provided.
Even before the legally binding children starting school will be offered a " Educación Prescolar " between zero and six years of age. This voluntary pre-school education is divided into two cycles: from zero to three years and three to six years.
Educación Primaria - primary school
From the age of six starts in Spain the compulsory education. During the first six years, the children go through a kind of secondary school, the " Educación Primaria ". Overall, this school is divided into three cycles, always have two cycles are summarized. For the students, this means that they can not sit each in the first year of a cycle. Only when the benefits are insufficient according to the second school year within a cycle, there is a repetition of the last school year. Certificates are however awarded after each year. It must be noted that the rating of one to ten, whereby ten is the best one for the worst performance. In the Primera students already learning a first foreign language.
Educación Secundaria Obligatoria ( ESO) - Middle School
At the age of 12 to 16 students, the High School, which serves as the basis for the professional and high schools to visit in Spain. In these four years, the young people can voluntarily choose teaching of a second foreign language. After completion of the ESO and thus compulsory education, there are two possibilities. Either you visit the two -year upper that leads to the " Bachillerato " and thus to higher education. Or you can select the " Ciclo Formativo ", the vocational stream. In contrast to Germany, there are the " Bachillerato " no separate audit, it is the grade of the final product.
In case of failure of the ESO, the student can under the " Programa de Garantia Social" first attend a secondary vocational school, are taught in the basic skills. Following this, he is given permission to visit the vocational stream.
Ciclo Formativo - Vocational Training
The vocational stream is used for training for all typical apprenticeships and takes place in special training centers. The training is mandatory nationwide to sixty percent, the rest lies in the decision of the Autonomous Region. After a theoretical education practical experience generally acquired in connection in an internship from an average of 200 hours. The contracts are concluded between training centers and companies.
For the professional training branch, there are two different levels: the " Ciclo de Grado Medio Formativo CFGM ", the basis of the professional training, and the " Ciclo de Grado Superior Formativo CFGS " the higher vocational education. On successful completion you reach the title " Técnico " or " Técnico Auxiliar ". You can build on, and then to achieve the title " Superior Técnico ", which offers the possibility to study in the same subject area. In Spain, thirty per cent of places are reserved for vocational branches.
Educación Superior - Higher Education
An academic education is in Spain to both the " Universidades ", the universities, the " Escuelas Técnicas Superiores ", the technical colleges, as well as to the " Escuelas Universitarias " that match the German Fachhochschulen about to be made. Also at the Spanish universities, there are restrictions on access. In addition, since 1975, entrance exams required.
The academic training takes place in three stages. After three years to reach the level " diplomatura ". Another five years it takes for the next stage, which leads to the " licencuatura ". Only after a further two years in the third stage and the constitution of a dissertation you reach the " doctorado ".
Of course, this list can not convey absolutely complete picture. In individual cases, you have to on the spot, depending on the circumstances, decide whether you want to send your children to a public or private school.
In addendum should also be noted that is issued in Spain, as in France, the lessons during the afternoon hours. This means that the children a lunch service within the school building. This is usually not too expensive. In addition, financially weaker parent can apply for a grant.