Eikonal equation
As eikonal ( Ancient Greek εἰκών eikon = image, likeness ) is referred to in geometrical optics the path of a light ray between the origin and destination; meanwhile, the term usually refers to the Bruns- eikonal.
Bruns- eikonal
The Bruns- eikonal or Brunssche eikonal is a function that the shortest path between two optical media by means of Fermat's principle describes separate points. It was published by the German mathematician Heinrich Bruns 1895.
Derivation of the acoustic wave equation as Hochfrequenzapproximation
Subsequently, the eikonal equation is to be derived as Hochfrequenzapproximation of the acoustic wave equation. So we go from the acoustic wave equation with the pressure, the position vector of location-dependent propagation velocity and constant density of
Wanted is a time- harmonic high-frequency approach for the frequency- independent amplitude and the run-time function can be assumed. It has the form
Because of the vectorial identity is also
The above equation can thus be written as
Division by then leads to
The above equation consists of three terms with factors which are dependent. For very high frequencies, the factor of the second term of the factor of the third term is then small, and even smaller. Same time, since neither the duration nor the amplitude are frequency dependent, the products of the second and third term for very high frequencies are very small compared to the first term and the equation is simplified to be
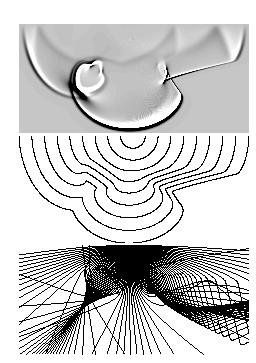
The solution of the eikonal equation assigns to each point in the spatial domain to the duration of the wave. Lines of equal duration can be interpreted as corresponding to wavefronts.
Others
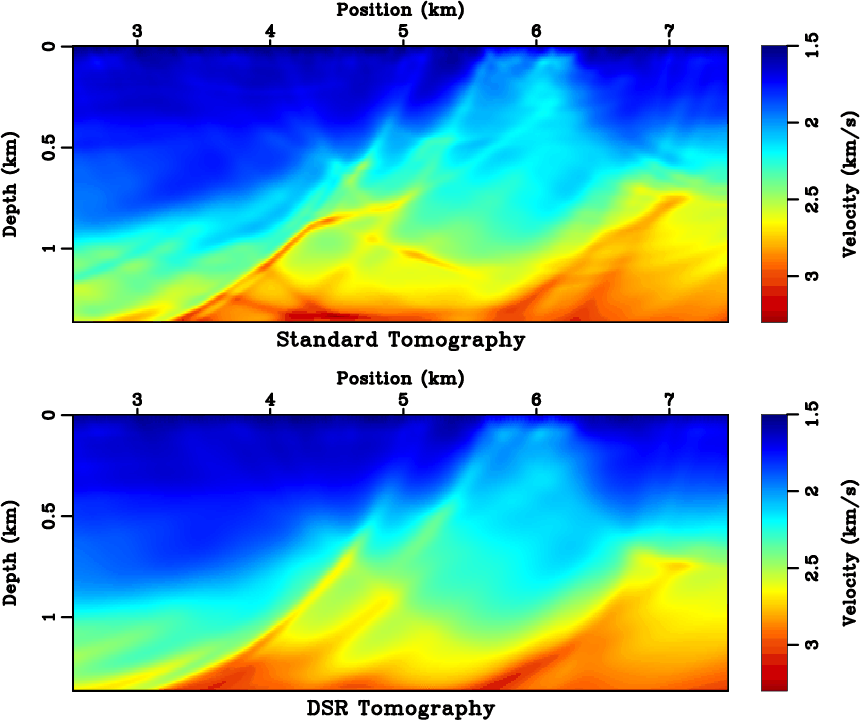
The Bruns- eikonal is also used in seismology to calculate the propagation of seismic waves.