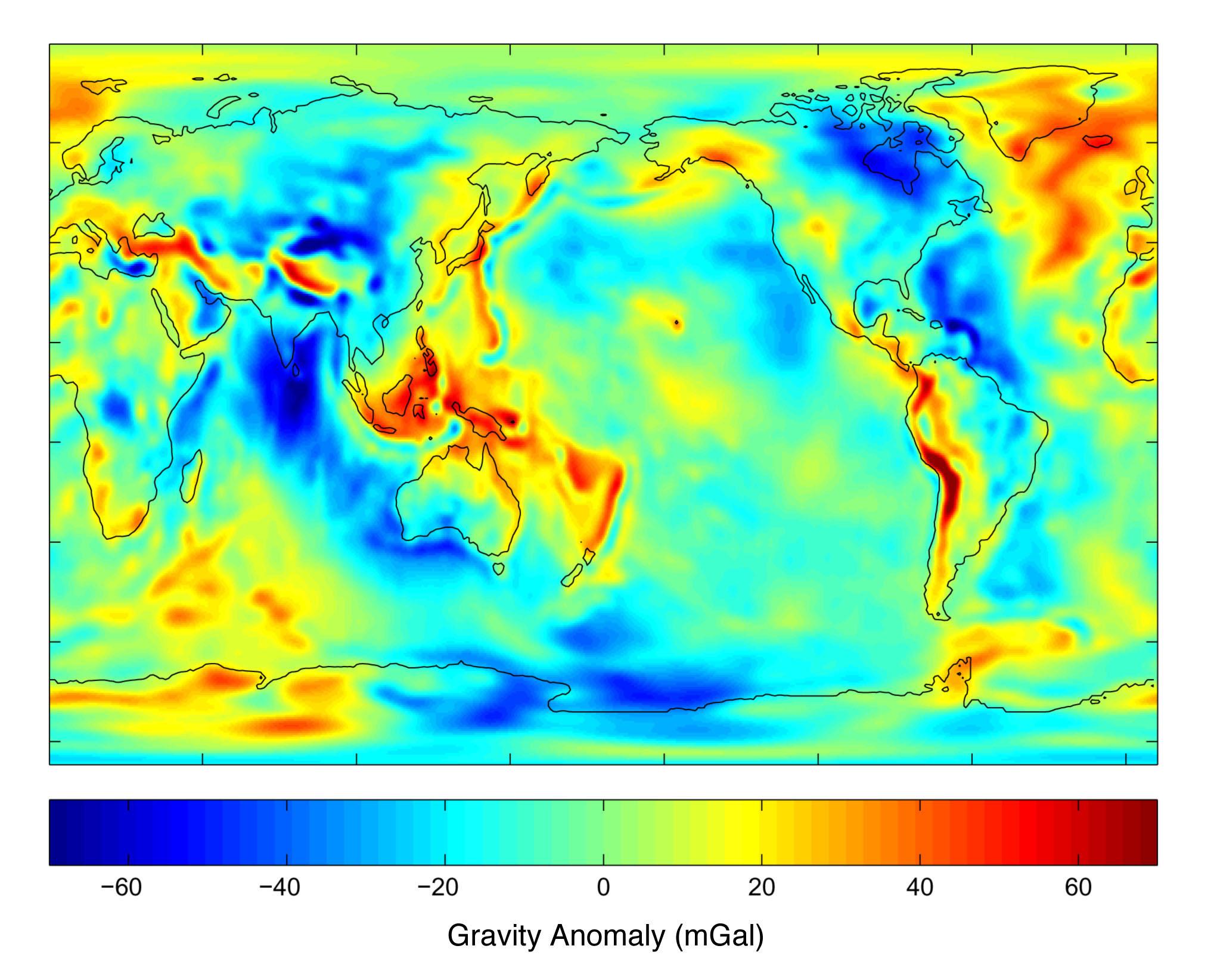
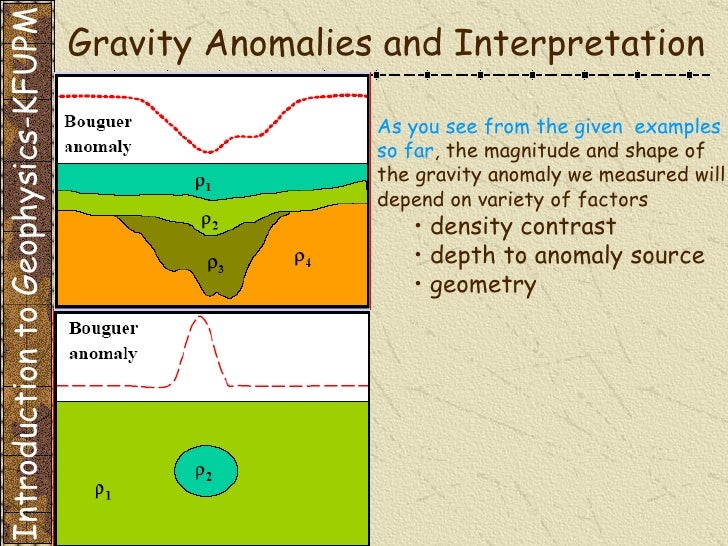
Gravity anomaly
A gravity anomaly (also called gravitational anomaly ) is the local deviation of gravity from the theoretical normal value on a reference surface, this is in the case of the earth usually the reference ellipsoid.
Causes of gravity anomalies
On Earth, gravity anomalies up to ± 200 milligal or 0.2 gal (0.002 m / s ² ) achieve what are 0.02 percent of the average gravity. They provide information on irregularities in the mass distribution in the subsurface, which can have several causes:
The former phenomena cause long-wave (regional) anomalies, while the aspects have 3-5 especially local characteristics.
Objectives of the gravity measurement
The measurement of gravity anomalies is often used for locating deposits. It is also a means to explore the deep structure of the Earth's crust, where it supports the methods of Geoseismik.
Another application is the geoid determination - the determination of the level of the Earth's gravity field. The geoid globally deviates from ± 50 m (maximum 110 m) from the Erdellipsoid and can be determined by well-spaced gravity measurements with dm- to cm accuracy.
For this and for other planetary satellite geodesy in particular comes into play, in which the orbits of artificial satellites are being tracked, which reflect weakened the gravity anomalies. The case required field downward continuation is, however, limited by the inverse problem of potential theory.
In flat lands, the method of deposit exploration by gravity measurements with gravimeters is particularly economical. In the mountains, however, the influences of the terrain are difficult to take into account the gravity. Therefore, seismic methods for detecting underground density variations there are cheaper.
Corrections and reductions of the measured values
In Gravimetriemessungen the acceleration of gravity is measured. The measured value is composed of the following components:
- Normal Gravity: Mathematical estimation of the gravitational acceleration at a point on the earth.
- Response correction: Correction of the temporally variable influences on gravimetric measurements. (mainly instrumental drift and earth tides )
- Width correction: correction caused by the latitude variation in the normal field. See International gravity formula.
- Heights or free- air reduction: the correction caused by different heights of the measurements above sea level variations.
- Bouguerplatte: Correction of the gravity effect of an infinitely extended plate of thickness h
- Topographic reduction: correction of the local gravitational attraction of the terrain ( mountains or valleys ); done with a digital terrain model.
- Share by density inhomogeneities in the subsurface.
In the literature there are different names for the corrections: so will take the correction also often speak of a reduction (gear reduction, Bouguer reduction, Bouger'sche plate reduction).
Conventional gravity anomalies
Bouguer
The Bouguer anomaly is reduced by all of the shares of the gravitational acceleration. It is caused by density inhomogeneities. You are in the ground below the reference level of Bouguerplatte. A positive Bouguer anomaly reflects a mass excess.
Free -air gravity
At the outdoor anomaly correction as in the Bouguer be attached, apart from the topographic Bouguerkorrektur and correction.
Analysis of gravity anomalies
There are regional and local gravity anomalies. The horizontal propagation of a gravity anomaly is often referred to as wavelength.
Local gravity anomalies extend only to small areas, they have short-wave abnormalities. Its origins are mostly flat-lying density differences. Regional gravity anomalies, however, extend over long distances, they possess long-wavelength anomalies.
Both of these abnormalities may be separated and form a mathematical model of the subsurface. However, these models are never unambiguous and must be supported by other investigations ( boreholes, seismic surveys ).
Examples of gravity anomalies
- Anomaly - T in Weddell Sea
- Münchberger gneiss mass
- Mascons of the Moon
Optical Illusions
In certain places it may by the nature of the surrounding terrain come to an optical illusion that results in the subjective impression of bodies (bottles, cars, etc.) moving without driving uphill - ie against gravity. This perception phenomena are sometimes referred to as gravitational or gravity anomalies, although this is not true.