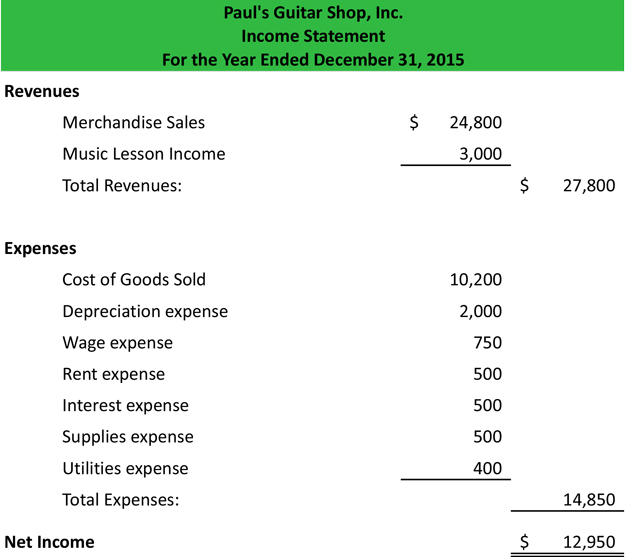
Income statement
The profit and loss account ( as the spelling HGB; orthographically correct, however, the profit and loss account, abbreviated P & L) in addition to the balance sheet is an essential part of the financial statements and therefore of the external accounting ( accounting ) of a company. It provides income and expenses of a given period, in particular of a financial year, and is thereby has the type, amount and sources of entrepreneurial success from financial engineering perspective. Preponderance of the income, the income is a profit, otherwise a loss.
Regardless of the profit and loss account, the ascertainment of the internal accounting system (cost and management accounting ) is to see that worked out the profit or loss based on financial ratios.
- 3.1 accounts or report form
- 3.2 gross or net principle
- 3.3 overall or cost of sales
- 3.4 Prior year amounts
- 4.1 Results Analysis and use of results
- 4.2 Success cleavage
- 5.1 HGB
- 5.2 IFRS and U.S. GAAP
- 5.3 Public administration
Legal foundations
According to § 242 HGB, the merchant has set up a comparison of the income and expenses at the end of each fiscal year. The Commercial Code and the tax laws and the international accounting standards ( International Financial Reporting Standards ( IFRS) and United States Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (U.S. GAAP) ) contain detailed rules on the formal structure and the contents recorded. The profit and loss account is subject to legal responsibilities for audit and disclosure. Only commercial partnerships and sole proprietors may waive a publication pursuant to § 5 of the Disclosure Act, if explanatory notes are attached to results of operations in a plant for the balance.
Monthly Income Statement
Many companies create each month a complete balance sheet and income statement and a few days after the end of. This gives update on the development during the financial year. Surprises after the end of the financial year are avoided, mistakes can be corrected at an early stage.
Financially relevant special incidents are properly distributed to the months. Examples: works holidays, major repairs, bad debts.
Income statement and balance sheet
In the profit and loss account of the success is determined by a " period of account "; account of all relevant performance data of an accounting period. From the " time account " of the balance sheet, the net Success can also by the status of the operating assets is compared on two consecutive dates. While the profit sizes in balance sheet and income are usually the same in the HGB financial statements, they differ in international accounting. Here, the P & L has a greater importance as a tool for presentation of results.
Formal structure
Accounts or report form
The profit and loss account can be constructed in the accounts or in the vertical format. The account form displays the result as the balance on the appropriate account page: On the downside for profit, on the plus side in loss. The report form matches the individual positions to each other and get to the net result of a continuation or continuation statement in several intermediate steps. Once selected, the form must be retained as a rule, deviations must be explained in the appendix. The report form (eg GmbH & Co. KG ) prescribed in § 275 HGB only for corporations and corporations & Co..
Gross or net principle
After netting the commercial law of expenses and income types must be listed as individual items in the profit and loss account. A netting, so the offsetting of income and expenses in advance, so that they no longer appear as a line item in the income statement is regularly archived. Exceptions are made for small and medium-sized corporations, which may be summarized specific positions in order to protect themselves from competition insight. However, this net principle mentioned method does not obviate the need for a detailed chart of accounts from which the netted components of financial performance must emerge.
Total cost of sales or
The calculation can be performed by two different methods: the total cost method ( SHI ) or the cost of sales (UCT ). Under German GAAP and IFRS are basically two options applicable. However, in IAS 1.92, the cost of sales method is compared with the total cost method is preferred because it provides information about features, despite considerable discretion in the allocation of expenses, which is classified as a decision-useful to users in relation to the total cost method. U.S. GAAP makes it compulsory for the cost of sales method. While the data base derived mainly for the full cost method of financial accounting, cost of sales is also dependent on internal accounting and requires a cost center accounting, or other appropriate detailing the accounts by function.
Although both methods start with the revenue for the respective periods. However, these revenues are based on different criteria assigned cost elements and adapted them to the statement of results. The total cost method takes into account all costs incurred in the accounting period under consideration in operational service, and provides them with all the proceeds realized. Since cost and revenue in the production of economic goods does not necessarily fall into the same period ( for example, goods are not sold necessarily in the same period in which they were made ), must, in this method the inventory changes on semi - finished and finished products (stocks to manufacturing ) are deducted to obtain comparable values for the determination of operating income. Specifically inventory losses are recognized as an expense and inventory increases as income. The same applies to the internal activities, ie, services that are not sold, but are consumed in-house. The cost of sales is based on the revenues of a period. You are faced only those costs which are incurred for the products actually sold ( cost of sales).
A second major difference is the grouping of the types of costs: While the total cost method is organized by type of cost ( material costs, personnel costs, depreciation and amortization), the cost of sales method groups the costs by function (cost center, production, sales, administration ). For a short-term, in particular for the monthly income statement, the functional decomposition is meaningful. Operating income for individual products or product groups can be determined so easily. The breakdown by type of cost is here but only after conversion and therefore not always possible pays basis.
If the assessment of the stocks according to the same criteria occurs, the calculation of net income results in both methods produce the same result.
Prior year amounts
In addition to the data of the current year are according to HGB and IFRS for comparison, the previous year's values specify the values of the past three years, according to U.S. GAAP. If a position ceased to exist in the current fiscal year, this inevitably leads to the empty headings. The opposite amounts provided must be comparable, otherwise explanations are accompanied in the Appendix.
Components
Results analysis and use of results
All income statement items listed below in accordance with § 275 HGB, from sales to the position of net income / loss for the year, are used to determine the company's success. Public companies have subsequently further information about the changes in the capital and retained earnings and thus on the amount of income to supplement ( § 158 AktG). This information, which may be made in the notes come from the dividend proposal of the Board. Under IFRS and U.S. GAAP of net income is not included in the profit and loss account, but goes into the changes in equity ( equity ) a.
Success cleavage
Both methods of recognizing income, provide for the calculation of net income to several intermediate results. Thus, the sources of success can detect and assess the profitability of the company realistic.
Under German GAAP, the "Income from operations " and the distinction " extraordinary result ". In the "Income from operations " table expenses and income that are typical for the operation of the enterprise purpose. It includes on the one hand, the operating result, which is originated from the statutory process of service, on the other hand, the financial result, the regular, but non-operating business comprises ( financing and investment transactions). The " extraordinary result " summarizes non-business success ingredients together. Among these unusual and rare incidents to understand that is not related to the actual business and not likely to repeat them. As can be expected from the results of operations, that it contains a recoverable on a permanent sediment can be assumed that a high volatility in non-operating results.
The most important components of success under IFRS and U.S. GAAP are the " result from continuing business activity " and the "Income from discontinued operations ". If a component of an entity, ie a division or subsidiary, closed down or sold, the result must be reported separately. This is also already when the task is scheduled sufficiently certain.
The intermediate results of each accounting standards are not fully comparable. An example: When a subsidiary is sold, the proceeds belong to the "Income from discontinued operations " in accordance with IFRS. Under German GAAP, it counts as a rule for " extraordinary result ". If such a sale but not atypical for the company, he is to "Income from operations " to be added. Generally valid comparison rules can therefore not be established.
Structure
HGB
According to § 265 and § 275 HGB, the profit and loss account must the numbered items listed below include (items are not included here). This is the minimum classification. A deeper subdivision is permissible if it does not affect the clarity and transparency; more items may be included if they are not covered by the compulsory items.
An outline shortening is only possible with companies for which no special forms are required. In addition, the amount must be insignificant, and the clarity of the income statement be increased by shortening. Small and medium-sized corporations are not permitted according to the cost method point 1-5, after the cost of sales items 1, 2, 3 and 6 balance and identify them as gross profit.
In Austria, the division by the UGB is regulated.
IFRS and U.S. GAAP
The international accounting under IFRS, compared to the HGB, lower requirements for the formal design of the profit and loss account. Placing it after the cost of sales, are additional information on personnel expenses and depreciation in the notes necessary. In addition, must be seen not only regular, but all significant income and expenses from the income statement or in the Annex; So it is especially important irregular components of financial performance (eg, impairment losses on inventories) shown separately.
In the U.S. standards, the profit and loss account represents the main tool of reporting; nevertheless knows U.S. GAAP as well as IFRS only a few rules for the formal structure of the income statement. The numerous information to be published can be listed usually alternatively in the profit and loss statement ( "income statement " or " Profit and Loss" (P & L)), supplementary tables ( " schedules" ) or in the notes ( the "notes "). The minimum information substantially conform to the IFRS classification system; the main difference lies in the mandatory disclosure of an extraordinary result.
Public Administration
In the public sector is called the profit and loss account and income. Another difference is that there is no equity in the income statement, but " net positions ".
Procedure for annual financial statements
The profit and loss account is assigned to a separate account in the chart of accounts, the " profit and loss account".
At the annual financial statements, the balances of each expense and revenue account are transferred to the profit and loss account. The overall result of these changes the balance of the profit and loss account must be in the same amount as in the calculation scheme presented above ( validation ) with correct accounting. Then the profit and loss account is completed on the balance sheet account equity. For profit, equity is increased, reduced in case of loss. Thus, the result of the profit and loss account is transferred to the balance sheet. The profit and loss account and its parent equity account connect the two accounts circles of double-entry accounting ( profit and loss accounts and balance sheet accounts ).
As a rule, all income and expenses in the profit and loss account must be detected, the comparison of the equity of two fiscal years shows the same corporate success as the result of the profit and loss account. Changes in equity that are not reflected in the income statement are deposits and withdrawals by the owners. These operations are not income or expenses, because they are not incurred in the business process of the company. In addition, there HGB only a few exceptions, the P & L neutral must be booked directly to equity: these include currency translation differences and the settlement of business or goodwill against reserves. IFRS and U.S. GAAP provide greater choice here, especially in connection with the valuation of fixed assets. Identify components of income that are not evident from the income statement is the task of changes in equity.