Inland sea
Inland seas (of Low German within: " within", not to be confused with inland lakes, which are among the inland waters ), are major side seas, each with a sea or ocean only by a very narrow strait ( strait ), respectively, in the opposite shore is visible with the naked eye ( sight).
- 3.1 Arctic Ocean ( Arctic Ocean )
- 3.2 Atlantic Ocean
- 3.3 Indian Ocean
- 3.4 Pacific Ocean
- 3.5 Southern Ocean ( Antarctic Ocean )
Waters discrimination
Definition
From the Inland Sea, the marginal seas that lie at the edge of a continent or ocean and are much less clearly separated from the latter differ. Both inland seas and coastal seas may be the Mediterranean at the same time.
In contrast to completely of a land area enclosed lakes that - apart from running waters - have no direct natural connection to the ocean, inland seas are not completely enclosed by a land area because they have a narrow strait on the zero meter contour line (including the above- mentioned line of sight connects from shore to shore ) with its adjacent main sea. Inland seas can be dependent seas of an ocean or other marine side.
For example, the Sea of Marmara at the same time an inland sea of the Black Sea and the Aegean. The latter sea is actually a marginal sea of the European Mediterranean, which is a Mediterranean and in turn is a huge inland sea of the Atlantic Ocean, because it is only by a very narrow strait ( the Strait of Gibraltar) connected to it. The Baltic Sea represents an inland sea of the North Sea, which is a marginal sea of the Atlantic. The Black Sea between Eastern and Southeastern Europe and the Middle East is an inland sea of the European Mediterranean or the Atlantic Ocean and the Red Sea between Africa and the Middle East is an inland sea of the Indian Ocean, where both the Black Sea and Red Sea are the Mediterranean at the same time as they There are between two different continents.
Erroneous use of the term
Not as an inland sea are the Gulf (eg Gulf of Finland ) or the Gulf (eg, Bay of Biscay ), because they are connected by a wide sea area with the respective main sea or separated only by a large mesh island chain of this - these are considered marginal seas.
Salinity
The salinity of an inland sea may differ significantly from that of the adjacent ocean, as the supply and / or discharge of salt water only via the relatively narrow strait that connects the inland sea with the ocean. Is the inland sea in relation to the width of the strait is relatively large, the salinity is mainly dependent on the ratio of the evaporation rate for freshwater entry through the leading- flowing waters and precipitation. This ratio in turn depends essentially depend on which there is air in the corresponding region.
For example, the Baltic Sea is a so-called dilution basin where the salinity is less than that of the oceans. Due to its location in a humid climate, the entry of fresh water from precipitation and rivers is generally high and evaporation is relatively low. This may be due to the low inflow through the Straits, which connect them to the North Sea and thus the Atlantic Ocean (see below ) can not be compensated. Therefore, the salinity of the Baltic Sea decreases even more slowly but steadily.
The Mediterranean, however, belongs to the so-called concentration pools where the salinity is higher than that of the oceans. Due to its location in a semi-humid to arid climate, the entry of fresh water from precipitation and rivers is generally low and evaporation is relatively high. This may be due to the low flow across the Strait, which connects it to the Atlantic ( see below ) can not be compensated. Therefore, the salinity of the Mediterranean rises even more slowly but steadily.
Examples of inland seas
Arctic Ocean ( Arctic Ocean )
Some of the White Sea is designated as an inland sea of the Barents Sea and the Arctic Ocean. Its opening to the icy Arctic Ocean is about 45 km wide.
Atlantic Ocean
Inland seas of the Atlantic Ocean are:
- European Mediterranean, connected through the Straits of Gibraltar to the Atlantic Ocean Marmara Sea linked by the Dardanelles to the Aegean Sea and the Mediterranean so that Black Sea (Eastern Europe / Southeast Europe / Western Asia ), connected by the Bosphorus and the Sea of Marmara and the European Mediterranean Azov Sea, connected by the Strait of Kerch to the Black Sea
- Baltic Sea ( Northern Europe ), connected by the Øresund, the Great Belt and the Little Belt through the Kattegat and Skagerrak to the North Sea
Indian Ocean
Inland seas of the Indian Ocean are:
- Red Sea ( between Africa and the Near East ), connected by Bab al- Mandab and the Gulf of Aden
- Persian Gulf ( Southwest Asia ), connected through the Strait of Hormuz and the Gulf of Oman with the Arabian Sea
Pacific Ocean
Inland seas of the Pacific Ocean are:
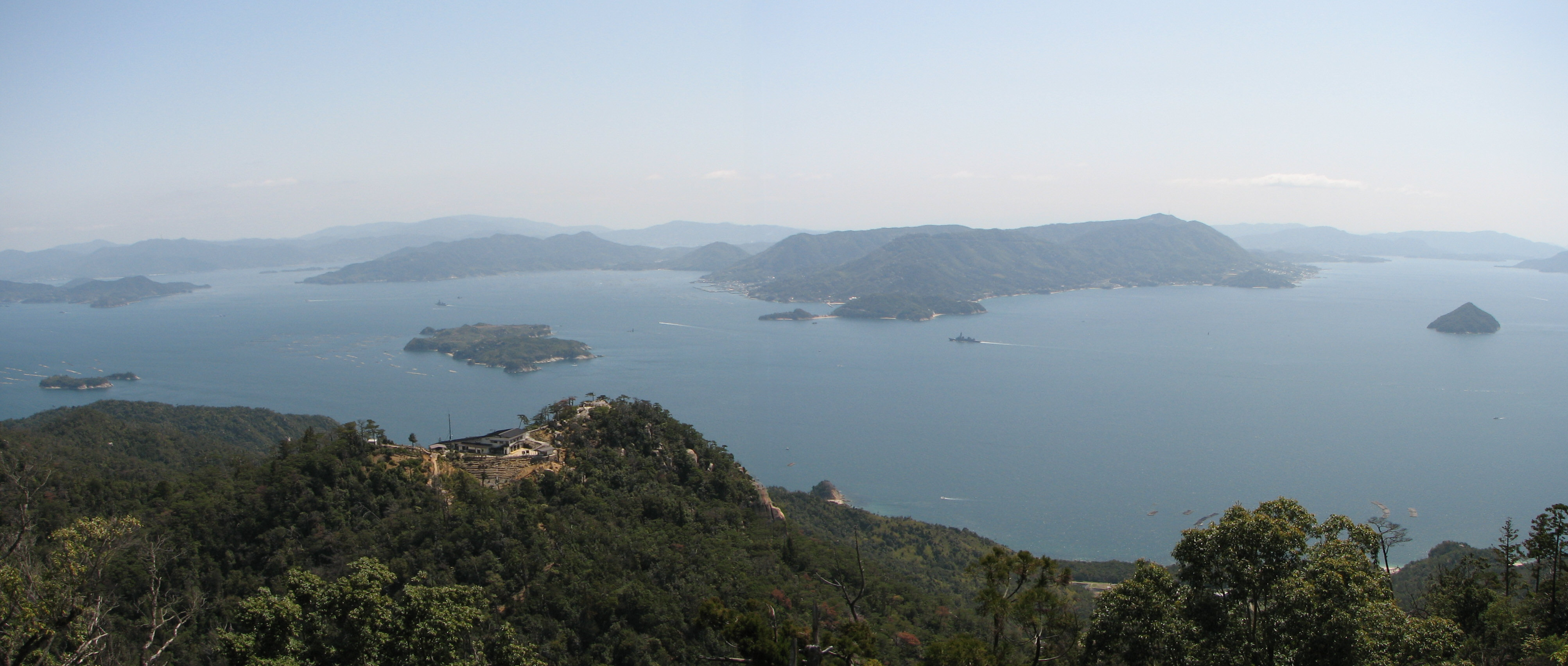
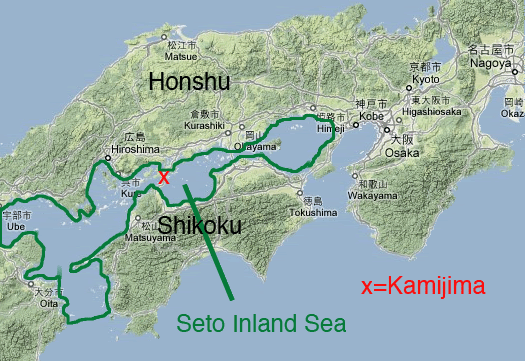
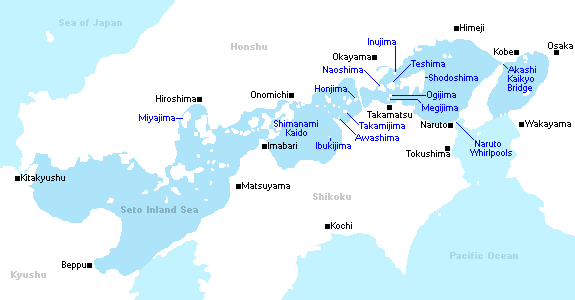
- Seto Inland Sea (Japan), connected by four different straits with the Pacific Ocean
Some of the Gulf of California is referred to as an inland sea of the Pacific Ocean. Here, however, is not considered that the opening is about 200 km wide. Thus one can speak of a strait or a visual link here on the definition of an inland sea barely. Therefore, it is a marginal sea of the Pacific.
Southern Ocean ( Antarctic Ocean )
The Southern Ocean has no inland seas.