Inverse-square law
The law of distance or distance law describes the amount of decrease of a physical quantity as a function of the distance to the source or the transmitter. Prerequisite is a free field without reflecting boundary.
For energy sizes - the 1 / r ² law
Among these variables include not only radiation intensities ( energy quantity ) eg X-rays, radioactivity, solar radiation ( visible light radiation ) or other in all directions propagating electromagnetic waves and the sound intensity.
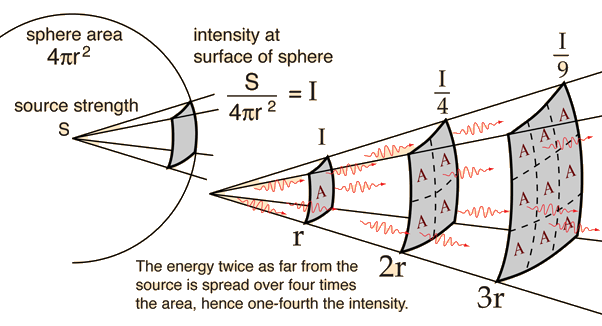
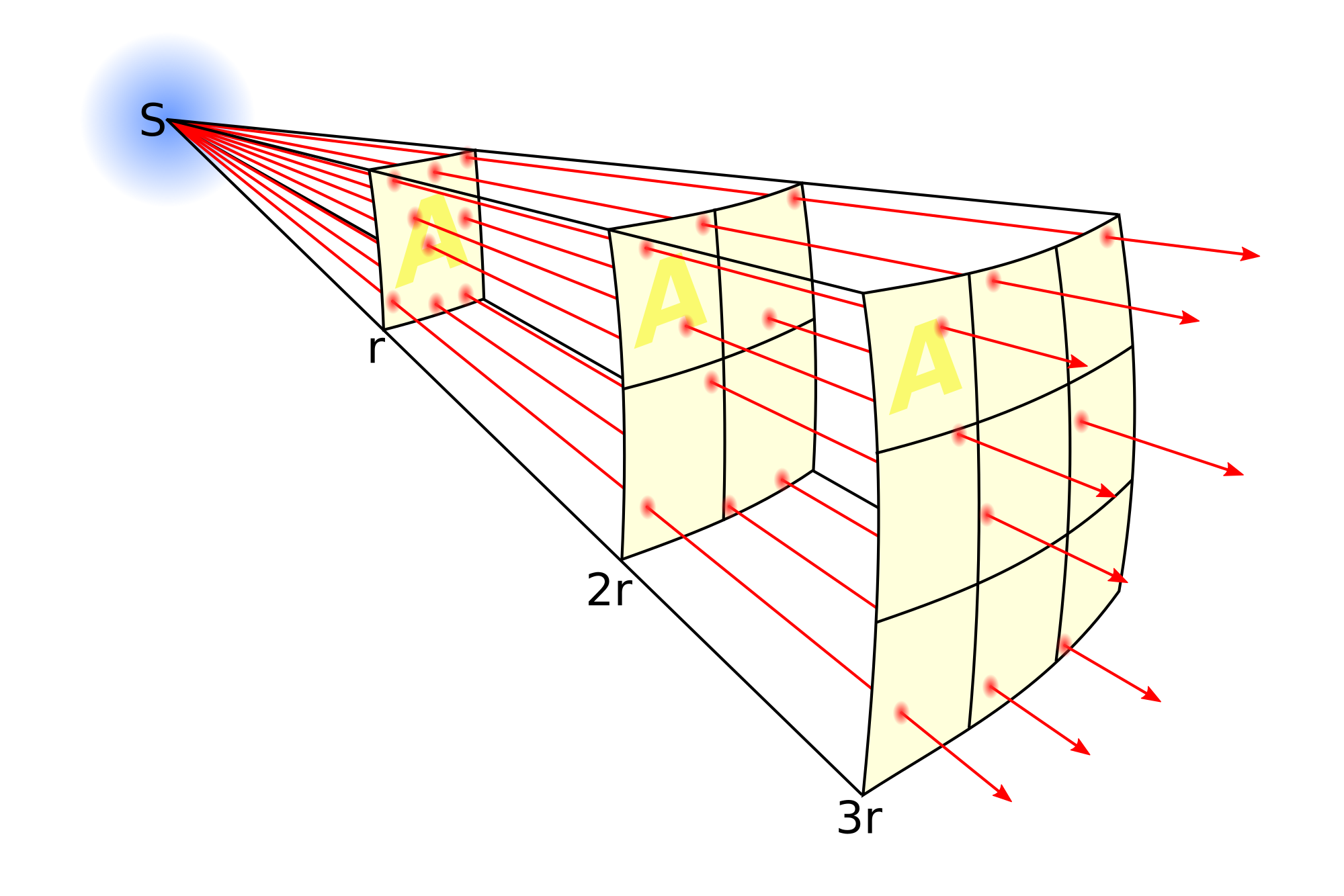
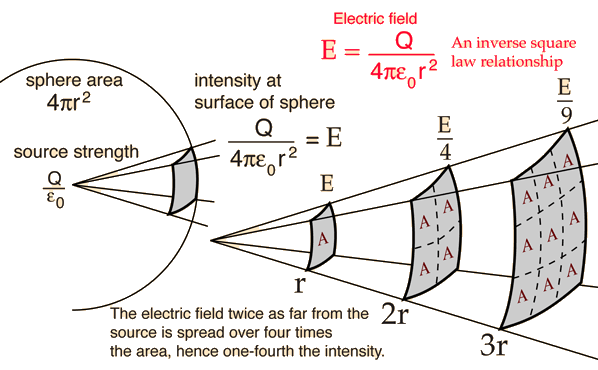
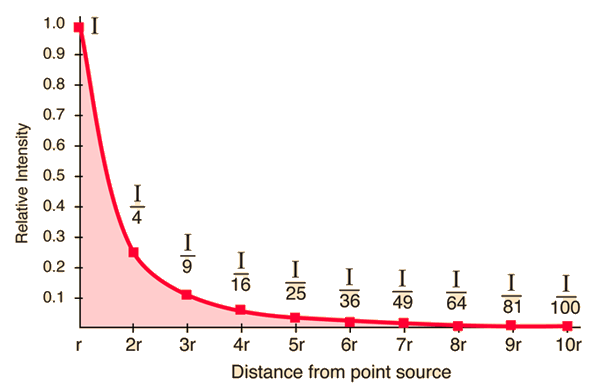
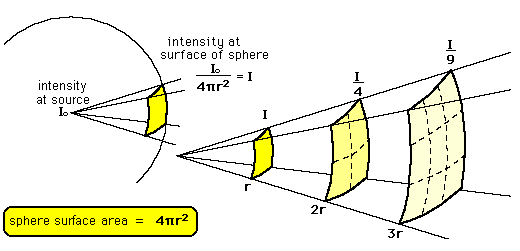
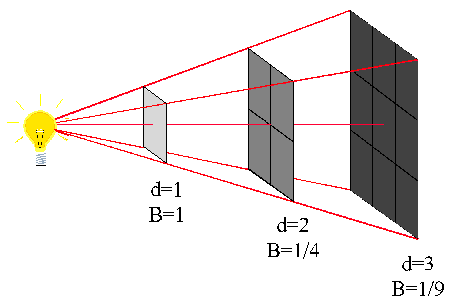
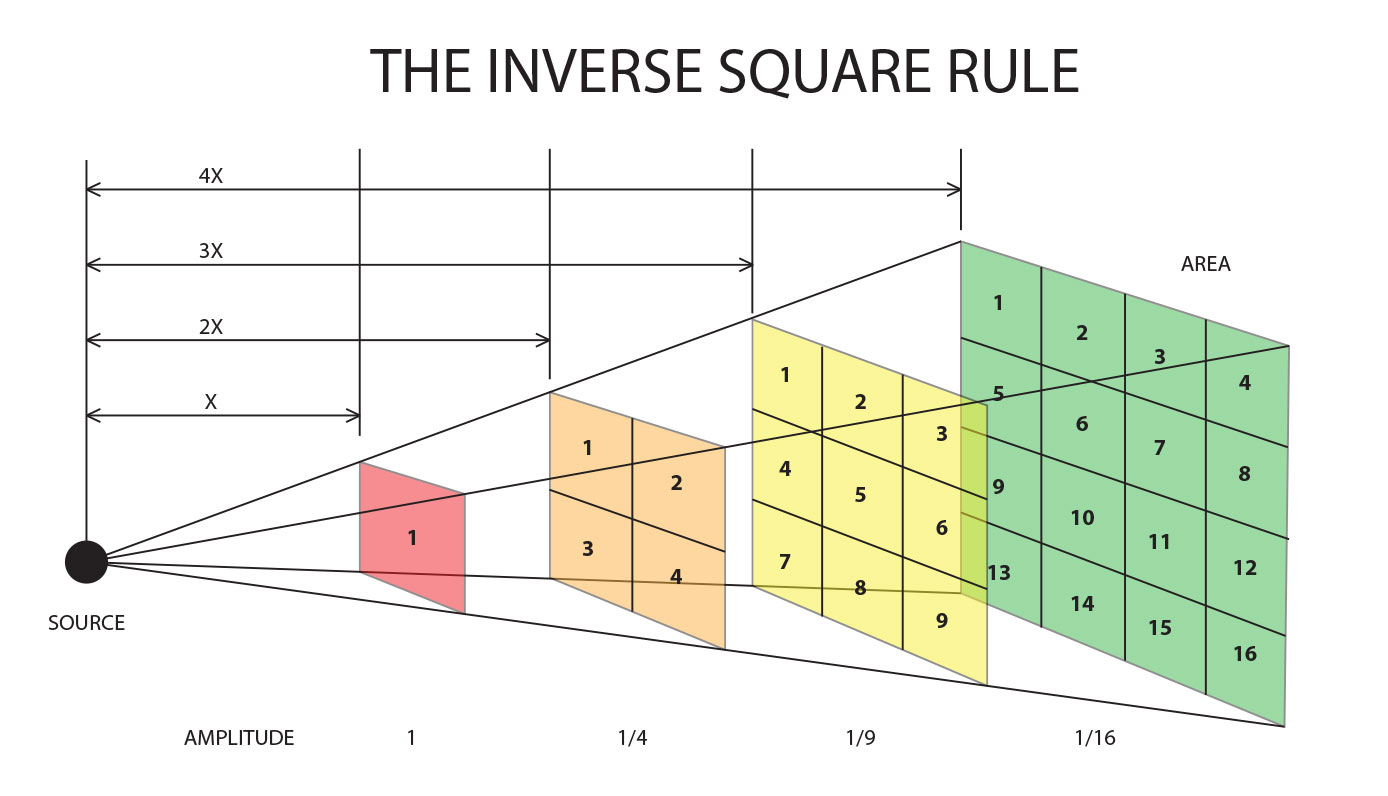
The energy E, which assumes a three-dimensional space in a uniformly radiating source, is spread over a spherical surface, which is proportionally larger with the square of the distance r from the source. The radiation intensity I, that is, the " power per unit area " (P / A), therefore, increases with 1/r2 from:
The intensity thus falls in the distance is doubled to a quarter of the initial value. This corresponds to a decrease in level by 6 dB.
In general, the level can decrease calculated as follows:
Or
Here lg is the logarithm to base 10
For effective values of linear field sizes - the 1/r-Gesetz
These variables include, for example, the acoustic field quantities such as sound pressure, sound velocity and Schallauslenkung as sound field sizes. The effective values of these quantities take inversely proportional with the distance from the sound source, that is, with 1 / R:
When the distance is doubled, the values thus fall to half of its initial value. This corresponds - as with the square sizes - a decrease in level by 6 dB. Thus, here goes for the level change in dB:
Or
Level changes can be given about ie without knowledge of whether it is the measured variable to a quadratic or linear size. For a determination of the physical units such knowledge must be available.