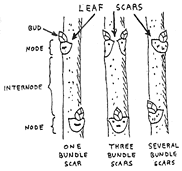
Leaf scar
Leaf scars occur on the stem axis of perennial plants after the fall of the leaves. They are particularly well visible directly after leaf fall. By converting the outer cell layers in a later lignifying Cutisgewebe fade the tracks in time, but are usually visible over several years. If necessary, the uppermost layer of cork can be removed carefully with a sharp blade to examine older scars. Since each type has specific leaf scars, these are in addition to bud and bark for the species identification of woody plants in winter is an important feature. You will always find below a bud. The leaf scars either sit flat on the branch, or on a more or less pronounced swelling of the branch, which is also called the leaf cushion.
Characteristic of leaf scars are next to outline the location and number of vascular bundles ( leaf traces or bundle of features). The vascular bundles in transporting substances between leaf and stem axis during the growing season. When the leaves fall, they rip and are in the form of dots or dashes usually clearly visible. In lane leaf scars only one vascular bundle is visible in several multi-laned accordingly.
However, leaf scars often form an entrance gate for plant diseases, such as when canker ( Nectria ) or the bacterial blight (Pseudomonas mors - prunorum ) at the cherry.