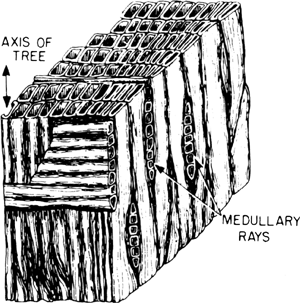
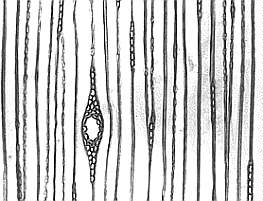
Medullary ray (botany)
Rays are part of the wood, passing through the xylem from the interior of the timber body to the cambium. They serve the radial supply of the wood body with water and nutrients. The wooden beams stretch across the cambium addition to the phloem, where they are called Baststrahlen.
Types of wooden beams
A wooden beam starts right in the pith of the wood, so it is called primary ray or medullary rays. If it starts in the xylem and not in Mark, it is referred to as secondary ray.
The single-row wooden beam in secondary vascular tissues is exactly one cell wide. The aggregated ray (composite wood beam ) consists of multiple cells.
Rays in hardwoods
For broadleaves, Rays composed only of memory cells. Depending on the type of wood they are single or multiple rows.
Only in some tropical wood species the arrangement of the rays follows a regular pattern. Also, resin canals, which are surrounded by epithelial cells, are found only in some tropical woods in the wood rays and are then often filled with white or dark ingredients.
Have wooden beams at Hardwood body a volume fraction of about 8 to 33 percent. There are also bushes with smaller rays.
Rays in softwoods
The structure of wood rays in softwood is much more differentiated than in hardwoods. For wood species such as pine, spruce or larch can always surrounded by epithelial cells, resin canals occur. The structure is either homozellular from parenchymal cells or heterocellular from Strahlenparenchymzellen and transverse tracheids.
Are located at the contact surfaces of the radial current Rays cells and the axial current Längstracheiden dots that allow a water and nutrient transport. These pits provide (as opposed to the wells in hardwoods ) Notes on the species of wood.
The volume fraction of rays on the needle wood substance is to one percent.
Functions
Contains the wooden beam no resin channel, it is used to transport water and nutrients as well as the storage of reserve materials. At the same time the Rays increase both the strength and the stiffness of the wood. Trees with many and thick wooden beams get less often longitudinal cracks.
Softwoods such as pine trees or yews that have no resin canals can, in the event of an injury form traumatic resin canals, by secreting parenchyma cells, which are called in their special function and epithelial cells or Exkretzellen, under high pressure resin in the wood beam.
Swell
Claus Matt Heck: Stupsi explains the tree. Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe. 4th Edition, Karlsruhe, 2010. ISBN 978-3923704729
- Wood
- Plant tissue
- Plant morphology