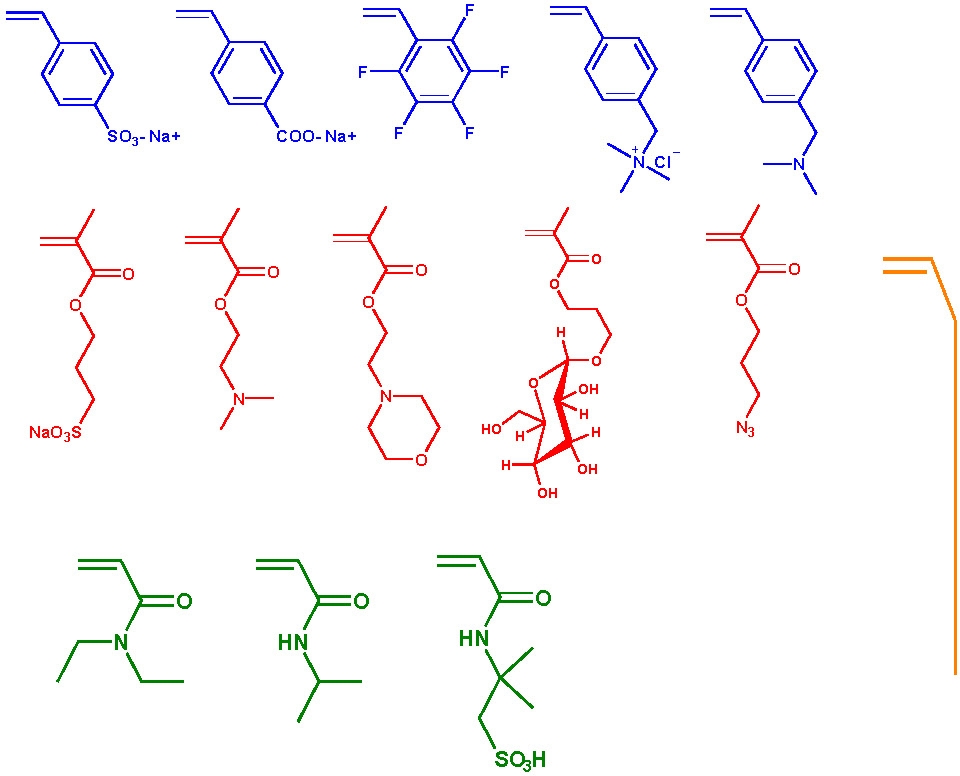
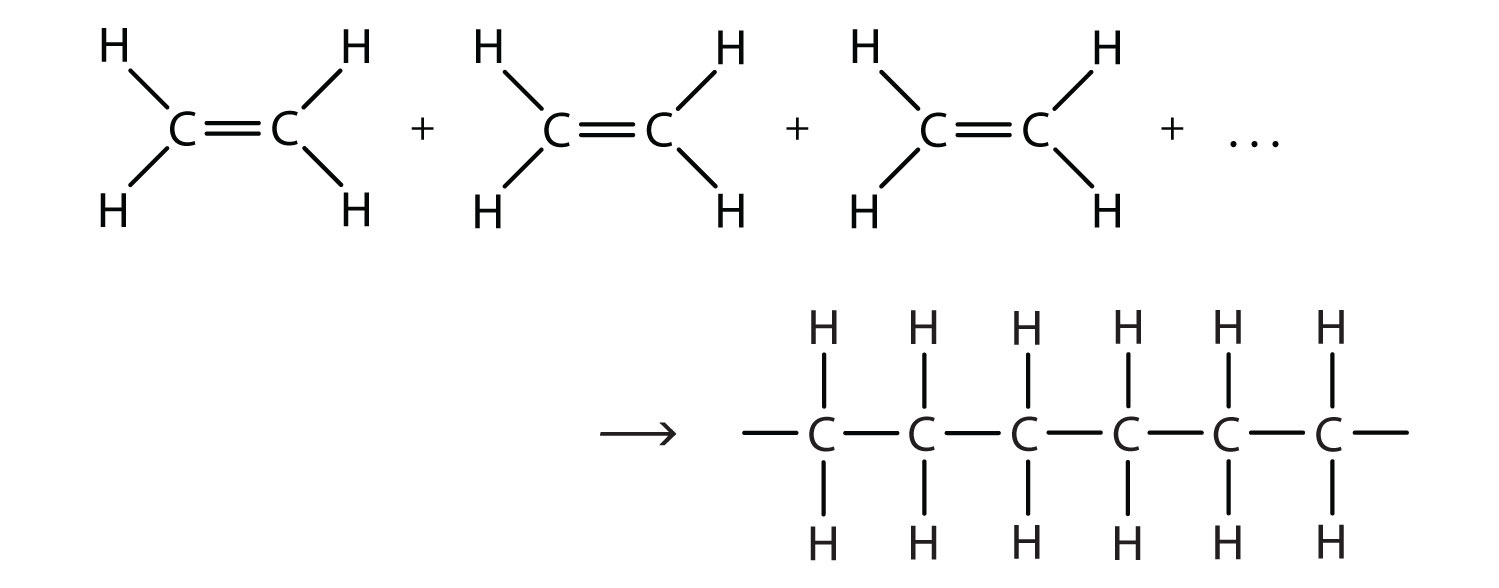
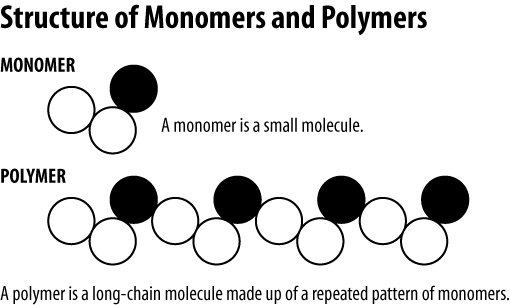
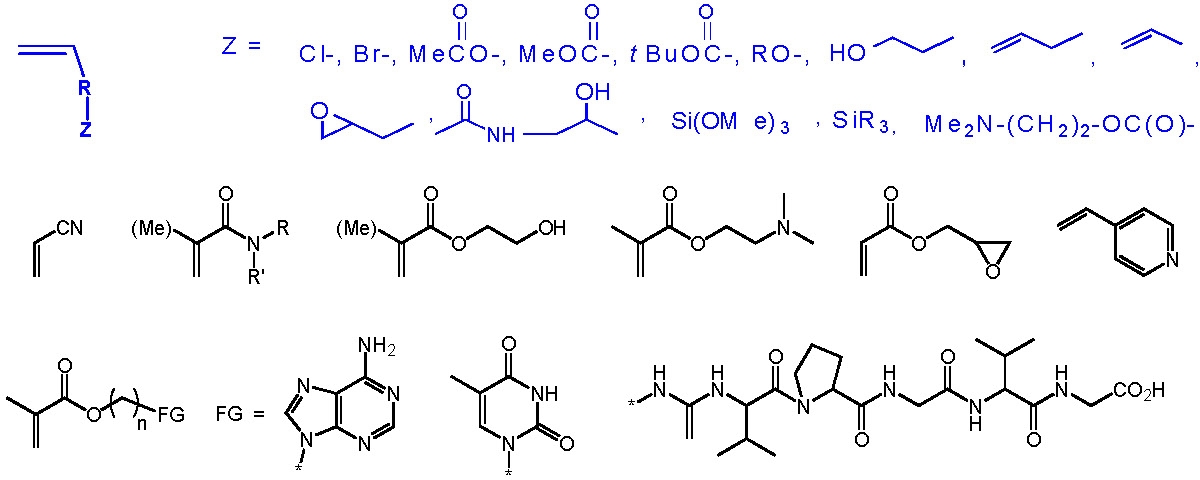
Monomer
Monomers ( ancient Greek μόνος monos, one ',' single ' and μέρος meros, part ', ' content ') are low molecular weight, reactive molecules that can join together to form unbranched or branched polymers. Monomers may be individual substances, but mixtures of different compounds. In the first case form homopolymers, copolymers in the second.
Chemistry
In polymer chemistry monomers are, in principle, all chemical compounds in which polymers can be formed via polymerization reactions. Monomers are often molecules with a carbon-carbon double bond or with at least two functional groups per molecule. Ring-shaped structures, such as caprolactam can be used as monomers for polymerization reactions. Monomers can be linked by chain polymerisation, polyaddition or polycondensation polymers.
There are inorganic monomers, such as the ortho-silicic acid H4SiO4, the polycondensation to polysilicic acids, see silicas.
Biochemistry
In biochemistry, the word " monomer" is sometimes referred to a sub-unit (also called subunit ) as a single component of a complex that is composed of several components. In connection with protein complexes are thus meant protein subunits that are associated non-covalently with one another. The subunits can associate or oligomerise or aggregate under suitable conditions via intermediates (dimer, trimer, tetramer, ...).