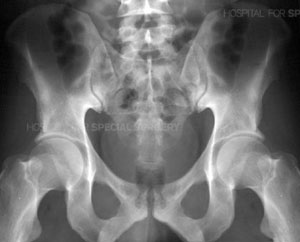
Pelvic fracture
A pelvic fracture is a fracture of parts of the bony pelvis. It occurs mostly in traffic accidents or from falls. Often the hip joint is involved ( acetabular fracture ). Internal bleeding in pelvic fractures are life-threatening.
Classification
A distinction (after Pennal and tile):
- Stable pelvic injury (type A): In case of breakage or breaks in peripheral areas (upper iliac wings, ischium, pubis, muscle origins ), the coccyx below the sacroiliac joint or at the anterior pelvic ring with bands obtained without strong shift
- Rotation Unstable pelvic ring injury (type B ): When displaced fracture of the anterior pelvic ring or symphyseal disruption, but stability of the posterior structures (even if involved). Type B pelvic fractures are often vividly called OpenBook fractures because the pelvic blades can be open to the outside in front of destroyed or symphysis pelvic ring.
- Rotary and vertically unstable pelvic ring injury (type C): In case of breakage of the sacrum or sacroiliac joint and simultaneously fracture of the anterior pelvic ring or demolition of the symphysis ( Malgaigne fracture ). Occurrence: Often in compression along the body axis
Unstable pelvic injuries are often associated with injuries to vessels, nerves and internal organs ( bladder, rectum, birth canal ).
Diagnostics
The inspection and sampling is to pay attention to local swelling and discoloration, misalignment, blockages in the hip joint, pulses and nerve function. To further exclude a life-threatening internal bleeding ultrasound is being used. To assess the bone structure X-ray plain films with optical path from the front, possibly also inclined rays are taken of 40 degrees up (to the caudal pool = Inlet) or 40-60 degrees down (toward cranial = basin outlet ). Frequently directly a CT or an MRI is being driven. The internal organs bladder, vagina and rectum manually by CT or MRI scan or, if necessary, examined endoscopically ( rare ).
Therapy
Stable pelvic fractures are treated conservatively. Under physiotherapy accompanied earliest possible mobilization is desirable.
Unstable pelvic fractures usually have to be an emergency basis stabilized by a pelvic clamp or an external fixator to stop internal bleeding by compression. Bleeding prohibit opening the pelvis. Later, the fractures are surgically fixed by plates or screws. Mobilization is possible after about two months.