Private network
Private IP addresses (abbreviated Private IP ) belong to specific IP address ranges that are not routed on the Internet. They can be used anywhere within private networks such as LANs.
Certain address ranges have been left for this private use of the public address space, so that local networks can be maintained without unnecessary administrative overhead. When the IP addresses of the Internet Protocol v4 were scarce and thus a conscious conservation of public IP addresses has become necessary, it was more important to have private IP addresses in the local networks. ( See also Port Address Translation and Network Address Translation)
Operation
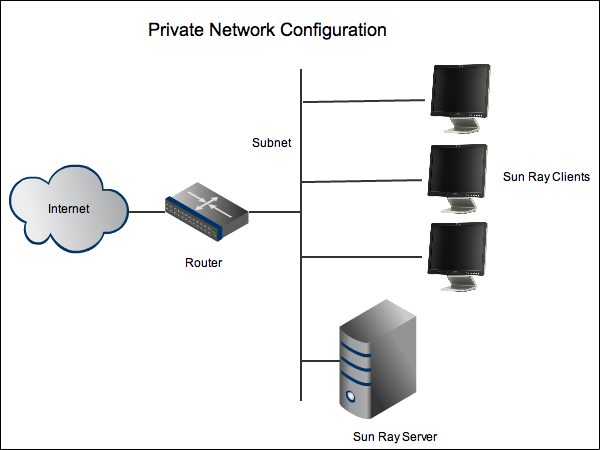
Although many computer networks require inside full connectivity at the IP level, but only a limited Internet access. When assigned to each computer that is connected to such a computer network, a private IP address, the computer network is an intranet, which can not be accessed from the Internet, as the Internet routers ignore the private address ranges.
A gateway or router that is placed in this private network and other than a private IP address on the private network also additionally has a public address on the internet can make the Internet for this private network. This can be done through a proxy or using NAT / PAT / masquerading.
Since the used private address range is always visible only within the private network, its address can be assigned in other private networks without the required by the Internet Protocol uniqueness of each IP address would be lost; in each private network in the global recessed address topics is the local address assignment, if at all because one has been configured.
Because the recessed address ranges are never routed, direct access is blocked from the outside to the local clients in the private network. This increases in an already properly configured firewall Although security is not on, but the concealment of local IP addresses outside the anonymous Internet access from the local network to some extent ..
When an administrator, however, a computer in the local network an IP address that is not from the specially reserved, private address space, but from the public address range will fail from the private network out any attempt to access an Internet host, to to this address has already been assigned in the Internet. The uniqueness of address assignment is violated. Instead, always access the local computer with the same address. From outside the local network, however, can be accessed without any problems on the computer set on the Internet. To forgive is not a private address in a private network and is therefore usually an error in its configuration.
Address ranges
From the IANA three private IP address ranges have been defined, which were documented in 1994 in RFC 1597. These determinations were in 1996 in the replacement of RFC 1597 by RFC 1918 are still valid today receive. Each of the three areas is in a different class to the historical net classes concept.
With subnetting, also only one part of a private address range to be used.
10.0.0.0 / 8
172.16.0.0/16 172.31.0.0/16 to
192.168.0.0/24 to 192.168.255.0/24
SharedAddress
Because of the address shortage and increasing conflicts with the IP address ranges listed above, another area for multiple use has been released. This area 100.64.0.0/10 RFC 6598 is specifically designed for Internet service providers for use with CGNAT.
Link Local
Further, the address space 169.254.0.0/16, which is awarded in accordance with RFC 5735 as Link Local, a similar special status. Using Zeroconf or Automatic Private IP Addressing ( APIPA ) can automatically use an IP address from this range devices.
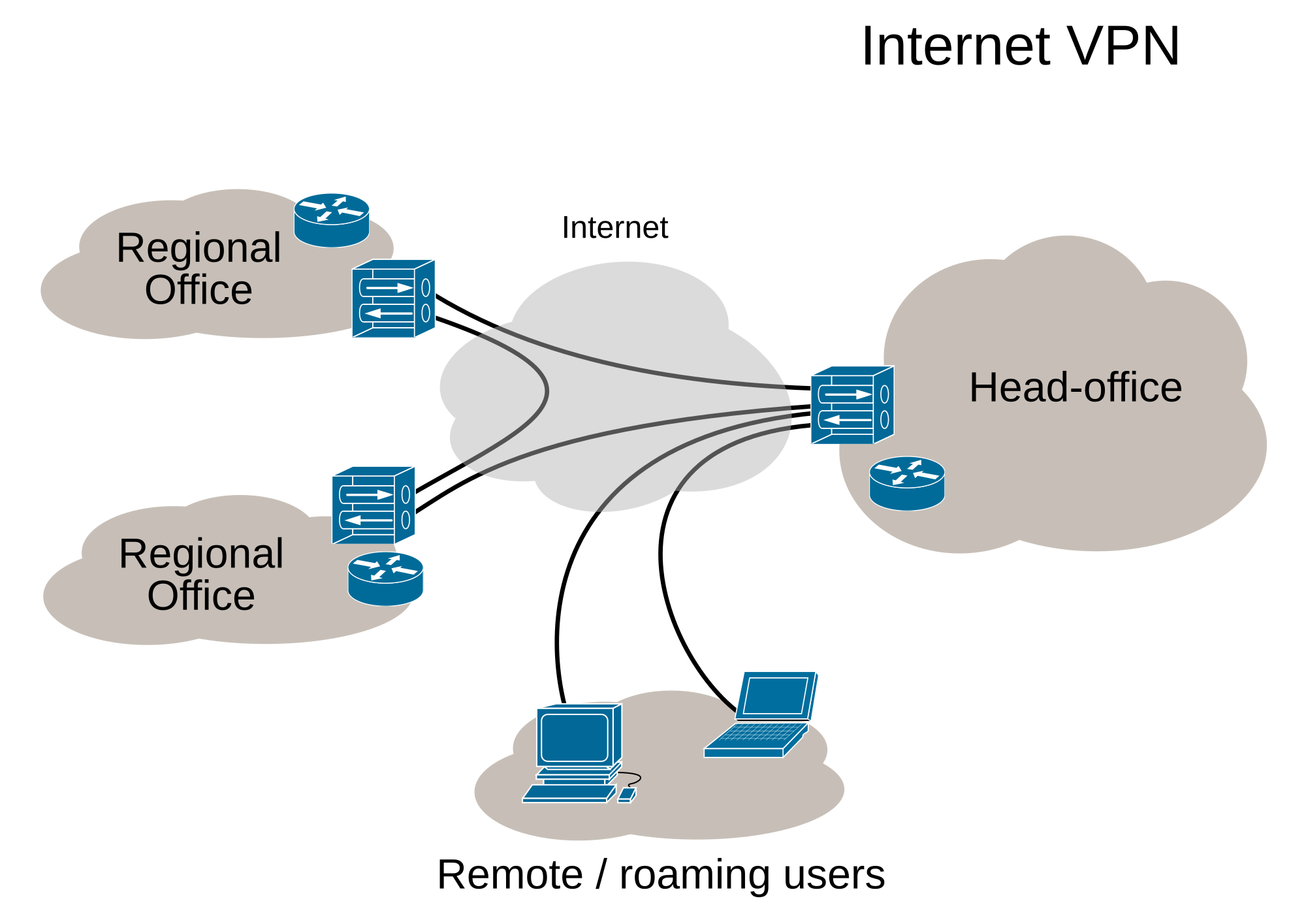
Address conflicts with VPN
The use of private address space regularly leads to problems when some corporate LAN via VPN are connected to each other, and both sites use the same networks. For only when the assigned addresses are different on both sides, no conflict occurs. This can be counteracted in advance by even when unconnected networks, the private address ranges of a corporate network considered and divided sense. When pooling of corporate networks, for example after a company merger, such planning in advance is not possible. This problem can be avoided entirely by public and therefore unique IP addresses are used, but at the cost of scarce public IP space.
IPv6
The IPv6 counterpart is called Unique Local Addresses. Because of the larger address space one uses there 40 bits of the network address as a random identifier. This should increase the probability of uniqueness of a private network to reduce address conflicts with association of private networks.