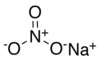
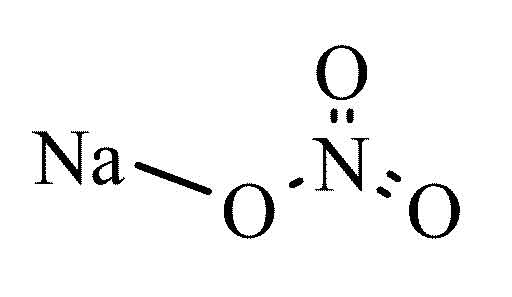Sodium nitrate
- Sodium nitrate
- Chilesalpeter
- Nitrate of sodium
- E 251
Colorless and odorless solid
Fixed
2.26 g · cm -3 ( 20 ° C)
306-307 ° C
Decomposition from 380 ° C
Slightly soluble in water: 874 g · l-1 (20 ° C)
Attention
1267 mg · kg -1 ( LD50, rat, oral)
Template: Infobox chemical / molecular formula search is not possible
Sodium nitrate ( Chile saltpetre or also sodium nitrate ) is a chemical compound the sodium salt of nitric acid. In the pure state it is in the form of a hygroscopic (water- attracting), white matter or colorless crystals.
- 4.1 food additive
Occurrence
Sodium nitrate is the most important naturally occurring nitrate. As a mineral, it occurs as niter. Main locality is Chile, hence the common name Chile saltpetre. The deposit in the Atacama desert are the remnants of deposited bird droppings ( guano ), the organic components are weathered. More natural occurrence, there is in Egypt, Asia Minor, Columbia and California.
Extraction
Natural occurrences are obtained by leaching with hot brine and purified by filtration of contaminants. Which crystallized in the cold sodium nitrate having a purity of about 98%. The iodate contained in the mother liquors goes into the Iodgewinnung.
Sodium nitrate can also be obtained by reaction of sodium carbonate with nitric acid:
Here offers the absorption of residual gases of ammonia oxidation in concentrated sodium carbonate solution:
For the oxidation of nitrite it is acidified with nitric acid, is oxidized in air to form nitrate and neutralized with sodium carbonate. In vacuum evaporators it is concentrated to a solid.
Sodium nitrate can also be obtained by reacting sodium hydroxide with nitric acid:
Properties
Physical Properties
- ΔfH0s: 15.5 kJ / mol
- S0s: 116 J / (mol · K)
Chemical Properties
In hot sulfuric acid, it is reacted to form nitric acid to sodium hydrogen sulphate:
At temperatures above 380 ° C it decomposes to sodium nitrite:
At temperatures above 800 ° C to sodium:
Use
- Fertilizers
- Building materials industry: cement additive
- Auxiliary in chemical drain cleaners
- Production of chemicals: potassium nitrate
- Formerly also to nitric acid production
- As a preservative E 251
- For the curing of meat and meat products (including sodium nitrite and potassium nitrite E 250 E 249 )
- PCM for thermal storage
Food additive
Nitrate is effective against bacteria, especially against the botulism pathogen ( Clostridium botulinum). When marinating process of chemically resistant little muscle pigment ( myoglobin) is converted into a more stable variant ( reddening ). As a result, the meat retains its red color. Ungepökelte meat and sausages take soon after slaughter to a gray color, by salting also looks old meat products fresh. In addition, when salting a typical aroma is formed.
Sodium nitrate is used for sausages, hard cheese, sliced cheese, pickled herring and sprat.
Nitrates themselves are harmless. The problem is their use because they are converted into nitrites. This transformation is in the food, but also in the human body possible. Nitrites are vasodilators and lowers blood pressure. In higher doses it can cause acute poisoning ( methemoglobin formation). Nitrite can be converted with simultaneous intake of meat or milk protein in the human body too strong carcinogenic nitrosamines.
Proof
- Sodium: bright as a light yellow in the blue Bunsen burner flame
- Solve spatula substance with dilute sulfuric acid and put a cold saturated with iron (II ) sulphate solution: Nitrate. Under-layers with a little concentrated sulfuric acid. At the boundary layer results in a brown ring, which is your proof of nitrate ( ring test ).
Swell
- Health Harmful substance
- Oxidizing substance
- Sodium compound
- Nitrate
- Food preservative

.jpg/640px-Chilisalpeter_(Sodium_nitrate).jpg)