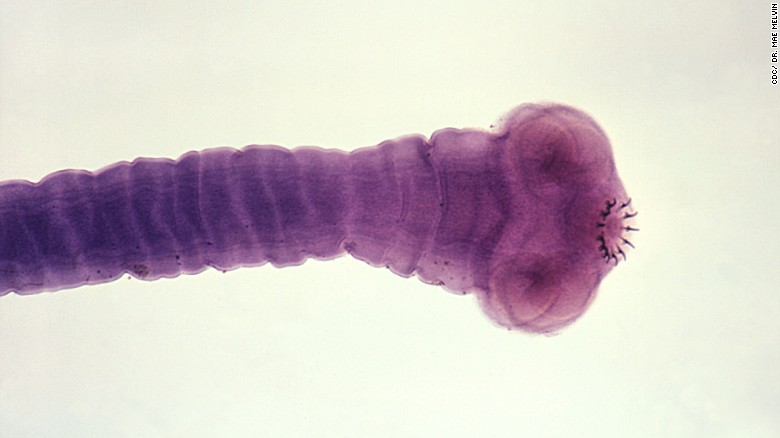
Tapeworm infection
The infestation by tapeworms, one of the parasitic infections, is relatively rare in industrialized countries in humans. Some tapeworms ( Cestoda, cestodes ) are among the human pathogenic, that is for the people disease-causing worms.
Survey
Among the pathogens you count
- Fish tapeworm ( Diphyllobothrium latum )
- Beef tapeworm ( Taenia saginata )
- Pork tapeworm ( Taenia solium )
- Small dog tapeworm ( Echinococcus granulosus )
- Tapeworm ( Echinococcus multilocularis )
- Dwarf tapeworm ( Hymenolepis nana )
Infection
A frequent localization of parasitic tapeworms living is the intestine. The secondary body covering ( neodermis ) as a special surface structure helps the worms to gain nutrients from the intestinal wall and thus to survive, as well as to adhere there and cause infection. In some cases, certain types of tapeworms can infect other parts of the human body such as the brain or liver.
Pathogenesis
The normal host cycle begins with the egg or fin of human intake. This may happen in different ways. In the various organs, particularly in the intestines, then the larvae develop and ultimately the adult tapeworms. These cause various inflammatory reactions in the organ systems and may metastasize via lymphatic and blood stream.
There are different types of human-pathogenic tapeworms, which differ in their pathogenicity. The fox tapeworm ( Echinococcus multilocularis ) for example, leads to the formation of cysts in the liver. Dog tapeworm ( Echinococcus granulosus ) can also trigger such Hydatidenzysten ( cystic hydatid disease ). More or less in all types of tapeworm infestation of humans occur nonspecific symptoms such as abdominal pain or itching in the anal region. The differential diagnosis of worm infestation should be considered in unclear abdominal pain into consideration.
Therapy
An efficient treatment of tapeworm infestation can be achieved with praziquantel and niclosamide. Praziquantel results in worms in advanced growth to paralysis, thus preventing further spread of the tapeworm. The pathogenicity of the worms is affected by it.
In cystic echinococcosis, surgical removal (resection ) is preferred primary.