Water activity
The water activity ( aw - value or even Activity of Water) is a measure of free water available in a material. It is defined as the quotient of water vapor pressure over a material ( p) to the water vapor pressure over pure water ( p0) at a certain temperature:
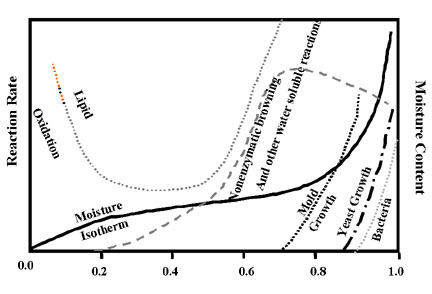
The aw value is an important measurement regarding the shelf life of food and affects the occurrence of the microorganisms ( spoilage ), which have different demands on freely available water. For lack of free water, the growth processes of some water-loving microorganisms are slow, sensitive organisms may even be killed, xerophile organisms, however, grow better with decreasing water content.
For most microorganisms the growth optimum is at an Aw of 0.98 to 1 However, there are microorganisms which tolerate a significantly lower water activity of up to 0.6 ( so-called xerophilic ). Examples are osmophilic (sugar- loving ) yeast or extremely halophilic bacteria.
The adaptation to low water activity is carried out by synthesis or uptake of compatible solutes.