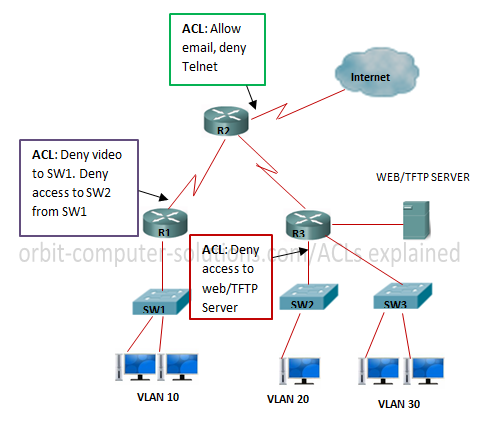
Access Control List
An Access Control List ( ACL) support, Access Control List German, is a software technique that can limit access to data and functions of operating systems and application programs. An ACL specifies the extent to which individual users and system processes access to certain objects (such as services, files, registry entries, etc.) have.
In contrast to simple access rights ACLs are fine adjustable. Thus, different rights are granted for a single file for multiple users and groups about Linux, while regular access rights only allow the assignment of permissions for a user, group, and the "rest of the world."
Unix and Linux
In the Unix world is meant by Access Control List an extension of the classical access control at the level of owner - group - world model. In this way, access rights may be specific to individual users assign or deny. Many UNIX implementations such as Solaris, IRIX and HP- UX led the early to mid 1990s, support for a very similar, designed as an extension of the classic Unix permissions model ACL model, and it was tried this ACL to standardize system under POSIX 1003.1e. The accompanying draft standard was withdrawn in October 1997.
Mid-2000 was begun to implement POSIX ACLs 1003.1e in FreeBSD and Linux. By now offer AIX, HP- UX, Linux, FreeBSD, TrustedBSD, Solaris, Trusted Solaris and IRIX native support for withdrawn POSIX ACLs 1003.1e.
Under Linux it ext3, ext4, JFS, XFS and ReiserFS file systems ext2 support, POSIX ACLs 1003.1e completely. With the KDE version 3.5 is also the Konqueror file manager with native POSIX 1003.1e ACL support. For the GNOME desktop file manager Nautilus dominated since version 2.16 native POSIX ACLs 1003.1e. POSIX ACLs are inherited 1003.1e statically in Linux, that is, the permissions are propagated into newly created subdirectories and files as needed continued. ACL is modified from a parent directory, but this has no effect on the underlying structure.
With RFC 3010 ( NFSv4 ) is a novel based on the ACL system of the NFS ACL standard was established in December 2000. Solaris, AIX, and Mac OS X now support this standard. The ZFS file system only supports NFSv4 ACLs.
Microsoft Windows
On Microsoft Windows NT 4.0 operating system each object (file, process, etc. ) is assigned a Zugriffskontrolldeskriptor which may contain an ACL. If no ACL exists, so each user gets full access to the object. Is the ACL exists but is empty, no user is granted access. An ACL consists of a header 1820 and a maximum of Access Control Entries (ACE). An ACE each contains the information whether a user or a user group in a specific type of access allowed ( allow) or deny (deny ) to be. The Windows Explorer writes the entries that deny access. At the beginning of the ACL Now when a user requests access to an object, the Windows Object Manager goes through the list from the beginning. Once entries have been found for all of the requested rights are allowed or denied access according to the Object Manager. Meets the Object Manager when going through the list to an entry that denies access, the search is aborted and denied access to the object.
For Windows NT version 4.0 ACL to be inherited static, Windows 2000 this is done dynamically on demand. ACL is a parent directory is changed, depending on the selected transmission this has an impact on the underlying directory structure.