Acinus
Acinar ( Latin acinus of " berry ", " grape", plural acini ) is the Latin term for berry glands, so the berry-like tail ( sero ) mucous gland ducts in which the secretion is produced. Characterized by it's large and dense epithelial cells with narrow lumen. In the lungs of the histological area is referred to as acinar, in which the oxygen exchange takes place.
Glands
In seromucous glands (eg, parotid gland ), it may happen that a so-called von Ebner shear Crescent ( serous Tail) resting the mucous tubule.
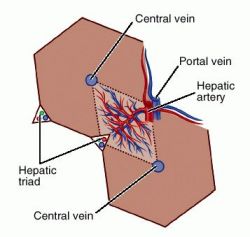
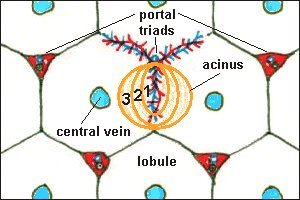
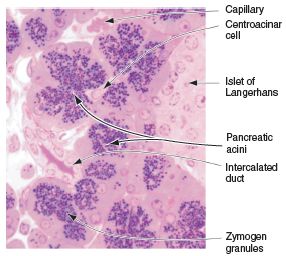
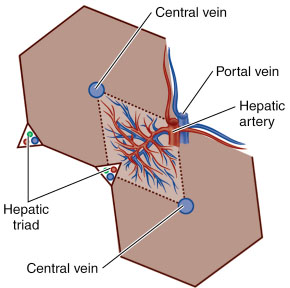
Acini are mainly found in the salivary glands and in the liver, lung and pancreas.
Lung
Starting from the terminal bronchiole to the airways convert respiratorii to the bronchioles, in which the alveoli are already to be found in the wall. Next, the respiratory alveolar reduce to the ductus. This will open themselves up to the final alveolar sacs. This is called tissue and all airways and alveoli, which are allocated to a single terminal bronchiole, as acinus of the lung. From the respiratory bronchioles takes place gas exchange. The acinus is the site of gas exchange, but has its epithelia, which produce the surfactant properties also a gland.