Acrylamide
- Prop-2- enamide (IUPAC)
- Propenoic
- 2- propenamide
- Acrylamide
Colorless crystals
Fixed
1.13 g · cm -3
84-86 ° C
241 ° C
0.9 Pa ( 20 ° C)
- Highly soluble in water (2040 g · l-1 at 25 ° C)
- Readily soluble in ethanol and acetone
Risk
Not determined, as carcinogenic
-212.1 KJ / mol
Template: Infobox chemical / molecular formula search available
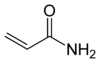
The acrylamide belongs to the chemical group of the amides. In pure form, it is a white, odorless, crystalline powder which is soluble in water, ethanol and ether.
Production
The preparation of acrylamide is carried out by hydrolysis of acrylonitrile with copper catalysts or by enzymatic hydrolysis.
Use
Acrylamide is used for the production of polymers and colorants. Noncrosslinked (co) polymers of acrylamide are usually water-soluble and are used as stabilizers or flocculants in many applications, for example in waste water treatment or papermaking. Crosslinked polyacrylamides are not soluble in water and swell to only; they are used as a carrier material in the gel electrophoresis (SDS -PAGE). Crosslinked copolymers of acrylamide and acrylic acid can be used as superabsorbents in diapers, for example.
Biological Significance
Details of the effect of acrylamide on human metabolism are still largely unexplored. Known from animal experiments are two modes of action: acrylamide reaches for a direct DNA at, on the other hand, it is converted by liver enzymes in glycidamide. This reactive species is attributed to a strong genotoxic effect. Acrylamide as well glycidamide form compounds with amino acids and nucleic bases and can thus change the structure and function of, for example, the DNA and hemoglobin. In animal experiments, the transfer of mutagenic effect was also observed in daughter generations.
In humans, despite many years of search no clear epidemiological results of increased cancer risk, on the contrary. The classification as a carcinogen based on studies with high doses of acrylamide in rats and mice (which, in contrast to people who roasts his food since time immemorial, grills, roasts and bakes, largely feed on raw food ). Recent studies found no increased risk of cancer ("no measurable impact" ), the cancer risk increased with increasing acrylamide levels in food even from. It should also be noted that only in the bloodstream spillage of acrylamide is relevant; recent studies suggest that the intake of acrylamide hardly in the diet to increased blood levels.
Acrylamide in food
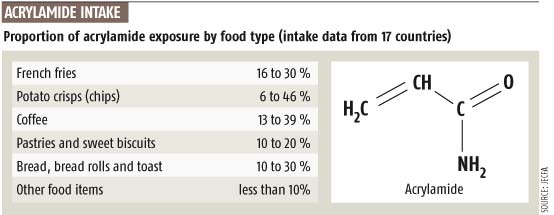
Acrylamide is since April 2002 in the headlines after it was found already in 1999 by Swedish scientists in various foods ( fries, especially in starchy foods such as french fries and strongly heated ).
Study at the Medical School of Hannover According to an increased acrylamide levels were only at those several times a week to eat French fries or potato chips, found in the blood. This is, however, " low and not significant from a scientific perspective. " For smokers were charged much higher. From the results it was concluded that not only the food, but " possibly endogenous degradation processes of proteins contribute to acrylamide gets into our bloodstream. "
Formation in food
It is formed in the Maillard reaction in case of overheating of starch, especially when baking, frying, roasting, grilling and frying. The primary source of acrylamide in food is the amino acid asparagine, which occurs mainly in potatoes and cereals. Acrylamide formation is promoted by sugars such as fructose and glucose.
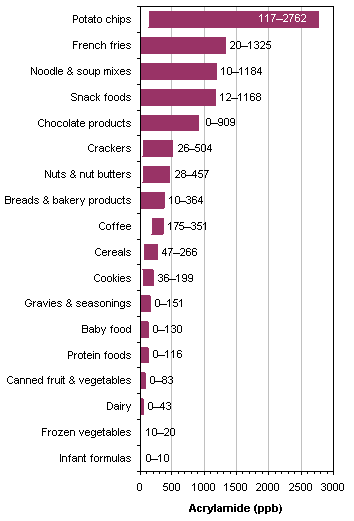
Especially much acrylamide is produced when potato and cereal -containing foods are heated above 180 ° C dry. However, the acrylamide formation begins at 120 ° C but increases rapidly at 170-180 ° C at. Here, a thin, dry layer, for example, the browned surface of fries or a crust of bread is enough. And so all the bread, crisp bread, French fries, potato chips, but also coffee sometimes contain high levels of acrylamide. For the potato is important to note that a Storage below 8 ° C exerts a stimulating effect with respect to acrylamide; At storage temperatures of 4 ° C, the fructose content increases strongly, resulting in higher acrylamide formation during frying and deep-frying.
Will you to the dry heating of foodstuffs not do without (→ raw food ), a wholly acrylamide-free diet is currently not technically possible. A threshold was not determined due to lack of knowledge about health effects in humans, for food. There are, however, annually signal values determined by the Federal Office of Consumer Protection and Food Safety, the competent authorities of the federal states with manufacturers particularly highly stressed products enter into a dialogue to minimize the values on the basis of. For example, in potato chips this signal value is 1.000 micrograms per kilogram. In a test of the magazine was Ökotest of 28 products tested, one above the signal value for acrylamide.
It is possible to reduce the acrylamide formation by a change of recipes and methods of manufacture. In many cases, already reduce the formation of acrylamide, a reduction of the maximum temperature when baking at 10-20 ° C, or replacement of, or waiver of individual ingredients. Thus, the Bavarian State Office for Health and Food Safety a high proportion of almonds and especially the raising agent ammonium bicarbonate (formerly ammonium bicarbonate, also: Hirschhornsalz ) identified as the main problem with gingerbread. After omitting the almonds and use of baking soda ( sodium bicarbonate, formerly sodium bicarbonate) in combination with disodium dihydrogen and dicalcium phosphate as a leavening of the acrylamide content dropped to one tenth of the previous value. However, these measures can adversely affect ( in part to a significant extent ) on the flavor and consistency.
In addition to these measures to reduce the formation of acrylamide (optimized material selection and treatment, and alteration of existing process steps ) and the development of new process technologies is conceivable, for example, the use of Vakuumfrittiertechnik in potato chip production.
Acrylamide in cosmetics
Acrylamide may occur as an impurity of polyacrylamide in cosmetics, but also as an impurity, for example, Polyquaternium-7, which is used in hair care products and shampoos.
Hazard characteristics
Although the International Agency for Research on Cancer in 1994 held that no sufficient evidence of human carcinogenicity of acrylamide are present, acrylamide has been classified as probably carcinogenic based on laboratory studies in rats and mice. It has the UN number 2074th
The WHO, as a general recommendation to acrylamide following statement: "There is not enough evidence about the levels of acrylamide in various foods is a general recommendation for the avoidance of any food to give. "
The Federal Institute for Risk Assessment notes
A) that "due to these differing results of studies included in the review can be neither accepted nor excluded that there are causal relationships between acrylamide intake and cancer development in humans. "
B ) " should be noted in this context that epidemiologically far no clear link between cancer and exposure to acrylamide was detected Perhaps the risk of cancer development is -. if present in humans -. practically at the given exposure barely detectable "
Acrylamide computing program
An approximate calculation of the individually recorded dose in entering the eating habits allows the BfR acrylamide computing program of the Federal Institute for Risk Assessment.