Aminobenzoic acid
The aminobenzoic acids form a group of substances derived from both the benzoic acid and the aniline in chemistry. The structure consists of a benzene ring with an added carboxy (-COOH) and amino (-NH2) as a substituent. Due to their different arrangement (ortho, meta or para), three constitutional isomers arise. The 2- aminobenzoic acid is known by its common name of anthranilic acid.
Properties
To the group of aminobenzoic acids include:
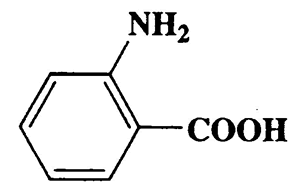
- 2- aminobenzoic acid (ortho- aminobenzoic acid ), also known as anthranilic
- 3 -aminobenzoic acid (meta -aminobenzoic acid )
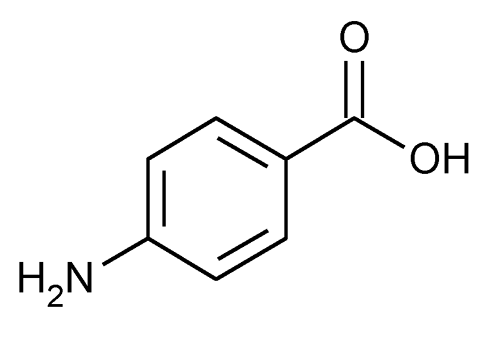
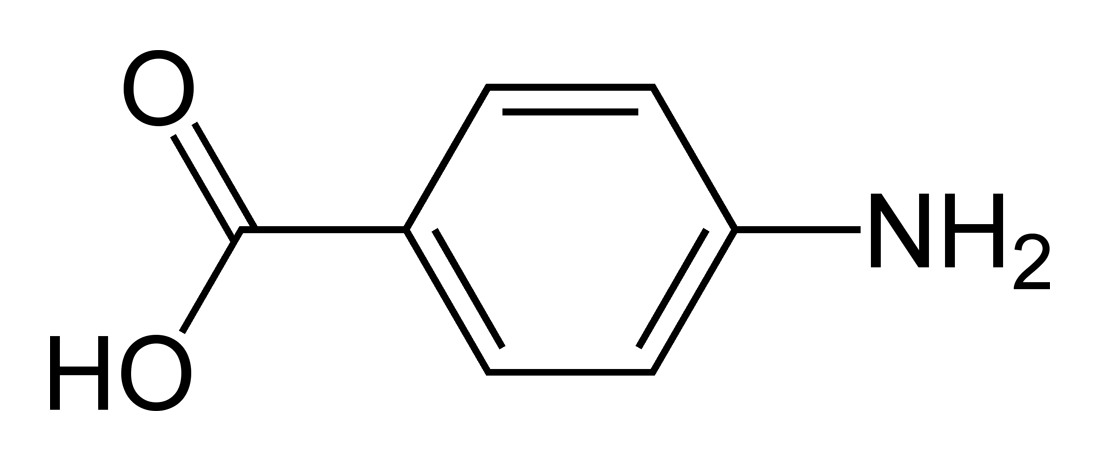
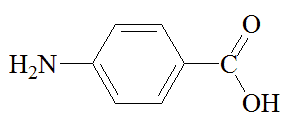
- 4-aminobenzoic acid (para- aminobenzoic acid ), also known as PABA
In comparison with aliphatic aminocarboxylic acids, the aminobenzoic acids are present in aqueous solution at a significantly lower proportion than zwitterions ( H3N -R -COO- ), since the basicity of the amino group on the phenyl ring is reduced.