Arc length
The length is in mathematics a feature that routes, paths and curves can be assigned. The length of a curve is also referred to as arc length or Rektifikationslinie.
- 3.1 Definition of the length of a curve
- 3.2 Parameterization of a curve to the path length
Lengths of routes
Are and two points in the ( two-dimensional ) plane of () with the respective coordinates and so the length of the route to the Pythagorean theorem is equal to
In the three dimensional intuitive space () with the respective coordinates and applies
There are essentially two ways of how to generalize such formulas:
- It interprets the length of the track than the length of the vector and defined length dimensions for vectors. The corresponding generalized concept of length of vectors is called standard.
- More generally, the approach instead of path lengths to consider the distance between the endpoints. General terms mean distance metrics.
Lengths of paths
A path is a continuous map of an interval into a topological space. To ascribe Because a length, this space but must have an additional structure. In the simplest case, the plane or the space of intuition, with the usual concept of length for distances; Generalizations are possible for Riemannian manifolds or any metric spaces. It then indicates the length of the path as well.
Way in the plane and in the space
A path in the plane or in space is given by two or three coordinate functions:
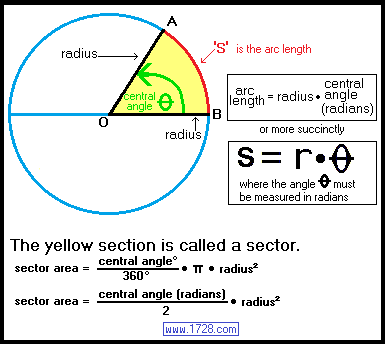
For piecewise smooth paths, the length of the path is given by the integral over the length of the derivation of the vector:
Motivation
The flat road is first approximated by short lines, which are broken down into two components, parallel to the coordinate axes. According to the Pythagorean theorem applies:. The total length of the path is approximated by the sum of all line segments:
Judging from the convergence of the facts and returns the result without exact limit calculation, so the length is the sum of all the infinitesimal line segments, ie: .
Physically, the integrand also be interpreted as a sum of the instantaneous velocity and the integration variable than time. This motivates the definition of the length of a path probably best.
Examples
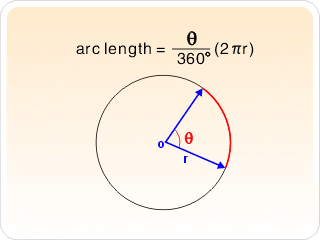
- The circle with radius
- A piece of a helix with radius and pitch
Special cases
Length of a function graph
Be the function of a differentiable function then calculates the length between the points and as follows:
Parameter representation
If the curve is given in parametric representation with and we pass up the parameters, then, the expression, the values of t to x = a and y = b are, this way:
( For L to write often s, then what is to be seen as without integral)
Example: The circumference of a circle can be calculated with the help of. A circle with radius satisfies the equation, or the derivative is:.
Applying the formula to, it follows:
Polar coordinates
Is a flat path in polar coordinates given, so
As obtained from the product rule
The length of the path in polar coordinates is therefore
Paths in Riemannian manifolds
Is generally a piecewise differentiable path in a Riemannian manifold, then one can define the length of a
Rectifiable paths in arbitrary metric spaces
It should be a metric space and a way in. Then is called rectifiable or enforceable, if the supremum
Is finite. In this case, is called the length of the path.
The length of a rectifiable path is thus the supremum of the lengths of all approximations of the way through distance trains. For the above considered differentiable paths, the two definitions of the length of match.
There are continuous paths that are not rectifiable, for example, the Koch curve or other fractals, space -filling curves, and almost certainly the paths of a Wiener process.
The word rectify or rectification means, just like you, that is the curve take ( the thread ) at the ends and pull apart, stretch out, so you get a route whose length you can measure directly. Today, this word appeared mainly still going on rectifiable. The term often used instead of rectifiable in the older mathematical literature is stretchable.
Lengths of curves
Definition of the length of a curve
Which belongs to a path image set is called a curve ( also track the way ). The route is also known as parametric representation of the curve or parameterization. Two different paths can have the same image, the same curve can thus be parameterized by different routes. It is natural to define the length of a curve as the length of a corresponding path; but that assumes that the length of each parameterization provides the same value. Clearly that is clear, and it can actually show for injective parametrizations. In particular:
Let and be two injective parametrizations of the same curve, ie. Then:.
Parameterization of a curve to the path length
As already mentioned, there are different parametrizations for a curve. A special parameterization is the parametrization according to the path length ( or arc length ).
If a rectifiable curve with the parameterization
And for the part of the curve with the parameterization, as one calls the function
As Weglängenfunktion of. This Weglängenfunktion is continuous and monotone increasing, even strictly increasing for injective and hence bijective. In this case, an inverse function exists. The function
Is referred to as the parameterization of the arc length as a parameter.
Is continuously differentiable and for all, there is a special feature of the parameterization by arc length that is also continuously differentiable and for all
Applies.