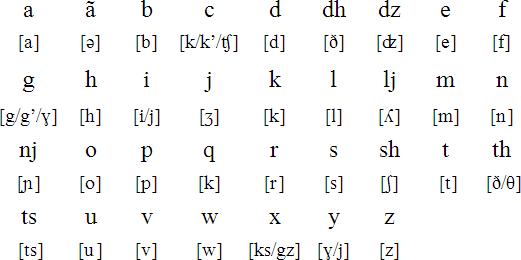Aromanian language
Spoken in
- Indo-European Italic Romanesque Balkanromanisch Romanian Aromanian
-
Rup
Rup
The Aromanian (also Makedoromanisch, self- designation limba armâneascâ ) is the language spoken by Vlachs on the southern Balkan Romance language or a dialect of the Romanian language. It is written in Latin or Greek alphabet depending on the country, a standardized orthography using the Latin alphabet has now enforced.
The ISO 639 code for Aromanian is rup.
Classification and language name
The Aromanian can be just like the Romanian, Meglenorumänische and Istrorumänische attributed to the Urrumänische or proto- Romanian, which in turn was developed from the Vulgar Latin Southeastern Europe. Together with these three languages, is it within the Romance languages the Balkan Romanic group in the narrow sense.
On the status of the Aromanian different views were presented. In some of the linguist, the four emerged from the Urrumänischen idioms are regarded as dialects of a single Romanian language due to their common origin, and said structural similarity. This view is still represented by a part of linguists. In the modern Romance languages , these four forms of speech ( Graur, I. G. Coteanu Giuglea, Al. ) Are classified as separate languages , mainly due to their long-standing socio- linguistic autonomy, so that the Aromanian in this view represents a separate Romance language. This thesis is also preferred by the Aromanians who gather in various centers ( Freiburg, Paris, Constanţa, etc.). The intention is to preserve this language.
As a language name next to going back to the proper name of some Aromanian linguists also Mazedorumänisch is used.
In other language sources and partly in the older Linguistics occurs for the Aromanian on the term Wallachian, Wlachisch or Vlachisch, which goes back to the foreign name of the neighboring peoples for the Balkan novels (Vlach ) and was also applied to the other Balkan Romance languages.
Dissemination and sociolinguistic status
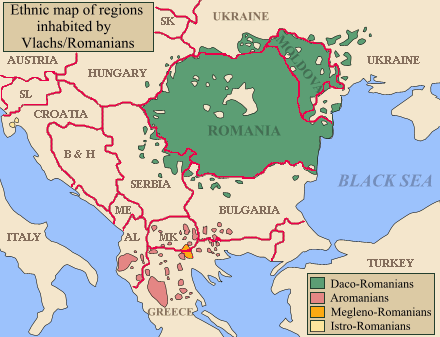
Aromanian is that of the Balkan Romance languages south of the Danube with the largest number of speakers. The distribution area of the Aromanian extends over large parts of the Balkan peninsula, and includes parts of Greece ( Epirus, Thessaly, Macedonia ), Albania, Macedonia, Bulgaria and Serbia. Because of emigration in the first half of the 20th century, a large number of Aromanians in Romania lives.
Today's numbers of speakers in each country be as follows:
- Greece: 200,000 speakers ( estimated by the Greek government in 1995)
- Albania: 45,000 speakers ( in 1995), scattered throughout the southern half of the country
- Romania: 27,000 speakers ( 2002 census ), 75 % of them in the Norddobrudscha
- Macedonia: spokesperson 8,467 ( in 1994)
- Bulgaria: 4,770 speakers ( in 2000 after WCD)
However, even where official data was collected through appropriate surveys or petitions, this information is not necessarily reliable ( as in 1994 declared in the Republic of Macedonia only 8,467 people as Vlachs, while the real number of speakers of Aromanian is estimated to be twice ).
The core of the Aromanian settlement area is now in the Pindus Mountains in North-West Greece to the city Métsovon.
Generally have the Aromanians hard to preserve their language, because there are no schools that teach in that language. Only in the Republic of Macedonia ( 8,467 spokesman, according to the census in 1994) they are recognized as a minority. In Romania, many so-called Vlachs call Romanians. The number of speakers is declining.
In Greece today there are still about 200,000 speakers ( as estimated by the Greek government in 1995). There, the Aromanian language is not recognized as a minority language. Political commitment to this language was hampered for a long time by judicial process. Even in the 1980s was a group of German linguists who made recordings for a Aromanian Language Atlas in Greece, harassed by the Greek police.
A larger group of Aromanian - speakers, probably on the order of 50,000 (TJ Winnifrith, in 1995 ), lives in Albania. When carried out in 2011 census, there were 3848 people Aromanian as mother tongue, which makes 0.137 percent of the total population.
The Aromanian is also spoken in other European countries, as are Canada, the U.S., Latin America and Australia, where the Aromanians arrived at different stages and to date form closed communities. Your actual total number is difficult to determine, because this aspect there is no thorough research.
In 1997, the Euro Europe has the Aromanian recognized as " worth protecting minority language".
History
After the conquest of the Slavs in the Balkans, the remains of Roman provincial population led a shadowy existence and operated remote pasture, rare transhumance. For these residues, the Vlachs were born. It is unclear whether it is at the Aromanians to descendants of Sermesianoi, Roman provincial population, which was 616 abducted by the Avars and settled in Pannonia. It may be argued that the Sermesianoi settled under the Proto Bulgarian Khan enveloping after their successful revolt to Thessaloniki, not far from the present settlement areas of the Aromanians.
In 1900 the Romanian state tried to build a aromunisches school system in several Balkan countries and to promote, which was, however, strongly influenced Romanian. In the meantime, there were 120 such schools. The Aromanian contains many elements of Greek, from the time of the Romanian funded schools also some dakorumänische elements.
Between the two world wars, a substantial number of Aromanians settled in Romania, especially in Dobrogea.
Syntax and Morphology
The noun distinguishes three genders, masculine, feminine and neuter in Aromanian. The Aromanian has as well as the Romanian five cases. The definite article is available as a suffix at the end of the noun. Both the specific and the indefinite articles are declined.
The verbs in the infinitive are not Aromanian. They are usually listed in dictionaries in the 1st person singular present indicative. The Aromanian, in contrast to other Romanian dialect languages also get the passé simple and the passé composé. The future is made with an auxiliary verb, the want of the verb is formed ( va), and does not change according to person and number: "va s- cântamu ", "va s- Cantata " (we will sing, you will sing, in Romanian: from Canta, Canta Veti ).
Example text, text comparison
Subsequently, the Lord's Prayer is on Aromanian:
For comparison, in Romanian:
In other versions, the words are replaced by: " fie " by " FACA - se "; " greşelile " with " greşalele "; " mântuieşte " with " izbăveşte "; " Ça a Ta este împărăţia şi puterea şi mărirea, acum şi în pururea şi vecii vecilor. " by " Ça a Ta este împărăţia şi puterea şi slava, a Tătălui şi a Fiului şi a Sfântului Duh, acum şi în pururea şi vecii vecilor. ".
Our Father in Latin: