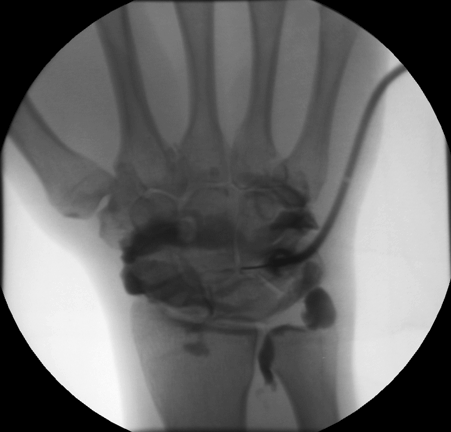
Arthrogram
Arthrography is a radiology examination method of joints. Before imaging techniques of ultrasonography, magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography were available, arthrography was the only way to represent soft tissue structures of the joints by means of an X-ray examination. For this, a contrast agent is injected into the joint. X-ray images are then made of different angles. By contrast, the nichtknochigen components of the joint on X-ray are now assessed.
As the use of cross-sectional imaging such as magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography can be reduced by the soft tissues and represent in the joints without the invasive arthrography. A further possibility for the display of the soft surface parts has the sonography. Arthrography has therefore lost in the X-ray examination of joints justified.
Same time, new applications for the arthrography have emerged with the development of magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography. Here, the injection of contrast media is used in the joint of the deployment of the capsule, and thus the better the assessability otherwise closely superimposed soft-tissue structures. Furthermore, some injury to the cartilage, the articular discs ( menisci ), the joint capsule and ligaments can be assessed safely only with the aid of a contrast injection. In particular, in the diagnosis of the shoulder joint and the wrist arthrography has again become a standard procedure followed by magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography.
Methods according to the type of the contrast agent
- X-ray image: arthrography with air or another gas (negative contrast)
- Magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography: arthrography with a water- soluble contrast medium (positive contrast)
- Computed tomography arthrography with air and a water-soluble contrast material (double contrast)
Risks
Arthrography is usually an investigation that is well tolerated by the patients. In considering possible contraindications and careful sterile procedure, the probability of the risks listed below is assessed as very low.
In contrast examination, the joint is punctured. This can, depending on the qualifications of the examiner, be painful. The joint puncture itself is a risk of infection, bacteria may be introduced into the joint, the resulting Pyarthros must be regarded as very serious damage to the joint. The contrast agent is typically in the X-ray examination jodbasiert and computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging when gadoliniumbasiert. Both types of contrast agents can cause allergic reactions.
- Diagnostic procedures in orthopedics and trauma surgery
- Imaging method (medicine)