Aspartate transaminase
- OMIM: 138 180
- UniProt: P17174
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST, ASAT, AAT) (formerly glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase gene: GOT) hot enzymes that catalyze the conversion of α -ketoglutarate in the amino acid glutamic acid. Without this reaction step, the malate - aspartate shuttle and thus the utilization of carbohydrates in the metabolism of eukaryotes would be impossible. Further, the reaction is part of the degradation of several amino acids, which is why the ASAT is found in all living things.
With the evolution of eukaryotes, a second isoform of ASAT was available. We distinguish cytoplasmic and mitochondrial ASAT (c- AST, m- AST ), with the corresponding genes GOT1 and GOT2. Plants have an additional form in the chloroplasts. Humans produce ASAT especially in skeletal muscle, heart muscle and liver. The ratio of c-ASAT/m-ASAT in the blood serum is indicative of the condition of the heart and liver.
Catalyzed reaction
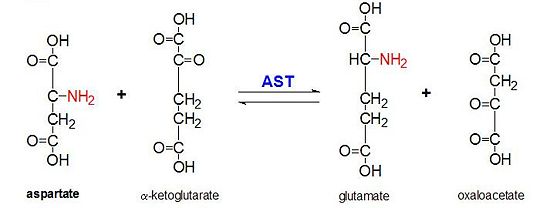
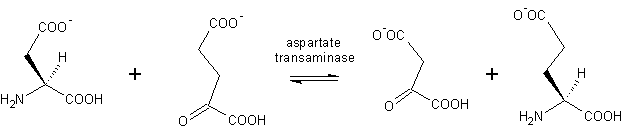
AST catalyzes the transfer of the general L- amino group of an amino acid to an α -keto acid. This is done, for example, the reaction of L-aspartate (1, see also Scheme standing ) α -ketoglutarate (2) ⇔ oxaloacetate (3) L- glutamate ( 4). ASAT needed ( vitamin B6 PLP, see ), which is bound as a prosthetic group of the enzyme for its function pyridoxal phosphate.
- OMIM: 138 150
- UniProt: P00505
Laboratory diagnostics
In the laboratory diagnostics, the activity of ASAT from the plasma or serum is determined in order to clarify whether a liver or biliary tract disease is present. The reference range for measurements at 37 ° C IFCC is < 52 U / l (Units per liter)
Increased AST levels in the blood are usually a result of liver or skeletal muscle disease or a heart attack. Increases parallel to the ASAT ALAT to that always points to a damage to the liver cells down (see De - Ritis quotient ). There is also in the red blood cells ASAT, one finds increased AST levels in hemolytic blood samples. This hemolysis may also occur in vitro by incorrect storage and long distance transport of blood samples. Large increases are found in all hepatitis as well as in toxic liver damage ( eg mycotoxins ). Under antibiotic therapy the ASAT are often elevated in otherwise healthy people. After the end of treatment, the levels drop back to normal levels.