Asset-backed security
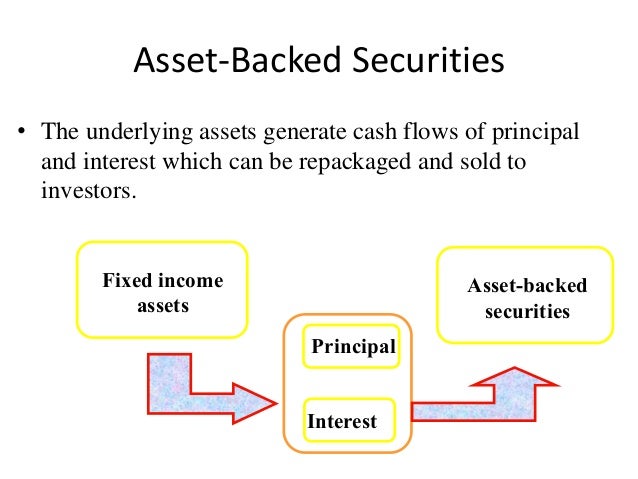
A forderungsbesichertes securities (english asset-backed security, ABS ) is an interest-bearing securities, which pay claims against a special purpose vehicle (English special purpose vehicle, in short SPV) has as its object, and wherein the special purpose funds used exclusively for the purchase of receivables usually several creditors and securitized to a security. The entitlements are covered which are transferred to the SPV by the volume of claims (assets ) ( backed ). In addition, the claims can be secured by each of the securities granted that are held by a trustee for the benefit of the holders of the asset-backed security. Seller of the receivables in such a transaction are usually banks that make loans as part of their tradable in order to raise money.
- 2.1 Creation of cash
- 2.3 capitalization requirement of the receivables at SPV
- 2.4 tax and commercial advantages
- 2.5 Regulatory Benefits
Operation
Asset - backed securities may be according to the true sale or synthetic sale method securitized.
Types
Almost all types of receivables may form the basis for asset-backed securities, provided they meet certain conditions. These include the transferability of the legal claim ownership, the generation of regular and clearly allocated to cash flow as well as historical performance data. Preferably in the pool financial assets are placed with average credit risk and a maturity of more than one year and promoted through diversification and over-collateralisation on a very good credit risk. Notably, these are receivables arising from loans, high yield bonds, mortgages, credit card transactions, licensing and franchise stores, other assets, leases and trade payables.
The term asset-backed security is in the jargon both as a generic term understood as well as a specific product group. Thus, a distinction is as follows:
- Asset-backed securities (ABS ) Term ABS
- Asset-backed commercial paper ( ABCP )
- Mortgage - backed securities (MBS ) Residential MBS ( RMBS)
- Commercial MBS ( CMBS)
- Collateralised debt obligations ( CDOs) Collateralised loan obligations (CLOs )
- Collateralised bond obligations ( CBOs )
Nature
With a transaction asset-backed securities tradable securities are issued, which supposedly represent a better risk due to the diversification of the underlying risk. According to German Federal Bank " sold a credit institution portions of its receivables to a special- for a specific or a plurality of such transactions company, which, in turn, through the issuance of securities, asset-backed security ( ABS), refinanced. "
Additional risk improvement
A further improvement in risk arises from additional fuses, so-called "credit enhancements " to hedge the transaction and improve the rating. Legally and economically sensible forms are the over-collateralisation ( Overcollateralisation ) at which the signal resulting from the demands of assets is greater than the nominal value of the securities issued; the distribution of asset-backed securities, senior and subordinated tranches ( subordination ) and the establishment of a reserve account (spread account), are deposited on the payment surpluses. Alternatively, the pool of receivables with a " cash discount" (Discount ) to the SPV can be transferred or a guarantee impartial third party, the receivable seller and an affiliated company or, for example, a credit insurance done. Demand failures of the underlying pool are intercepted by these security mechanisms. Apart this failure backups are also used liquidity facilities that are drawn only on the basis of market disruptions or liquidity problems. accessible is the formation of a liquidity reserve by a "back-up " line. Frequently, two or more forms of security are combined, with the aim always to find the best trade-off between the rating improvement and increase the cost.
Advantages and disadvantages of the transaction for a bank as a receivable seller
Creation of liquid resources
The value of the receivables sold, the bank receives as cash and can now be profitable for them. For one, they can use this to reduce liabilities. Thus it achieves a balance sheet reduction and the increase in the equity ratio. Through the on-balance sheet sale, they also improved their rating, thus achieving lower refinancing costs. The cash can be reinvested in higher yielding products.
The capital cost of a financed through asset-backed securities investment are lower in comparison to traditional debt financing. This is due to the " true sale " reached independence of the credit quality of the underlying pool separated from the selling financial institution. The sale of the receivables and the risk of default by the SPV is transmitted. The regulatory capital relief that comes with this risk transfer is the most important reason for the use of asset-backed securities. For the loans sold, the Bank is required to maintain function of the guarantor less or no more liable capital.
Disadvantages of asset-backed securities transactions resulting primarily from the complicated structure and the associated costs. For a cost-recovery operation interest received on loans must be sufficient to cover the capital market interest rates to the investors as well as the costs of the transaction. When selling the bank go natural also interest received on loans sold lost. Condition for the desired capital relief is a " clean break ". This means that the Bank may from the receivables sold no default risk more grown up when the credit debtors are insolvent.
Another disadvantage of asset-backed transactions, the expense associated with them. They cause investment and running costs, the fixed cost is very high. Only at a high level of capital ABS are economical.
Capitalization requirement of the receivables at SPV
To achieve the desired positive aspects for all parties is a prerequisite that a transfer of the receivables is in the assets of the SPV and thus a separation of the credit risk of the underlying exposures of the credit risk of the selling company ( originator) is guaranteed. Consequently, it is ensured with this operation that the exposure- buying SPV is not included in the scope of consolidation of the originator and thus the capitalization requirement of the claims in the SPV is located.
Tax and commercial advantages
Advantages also result from the German commercial and tax law. Instead of an actual sale only the credit risk through a credit default swap is made. Thus, the trade tax attributable to the interest income of the SPV.
Regulatory advantages
The German regulatory law ( until the entry into force of Basel II) provides incentives for the use of ABS. Default risks have to be backed by equity. The backing can be significantly reduced through the securitization of receivables with good credit. This process is also called regulatory arbitrage. Supervisors recognize the shift of loans from the portfolio of the originator to the SPV only if the risk transfer actually takes place. This means that the originator then look no further responsible for ensuring that the requirements are met ( clean break ).