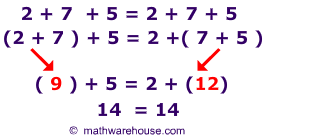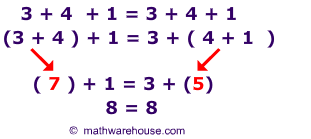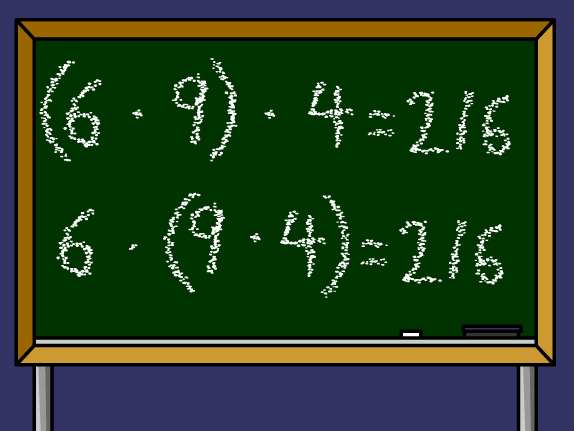Associative property
The associative law (lat. associare " unite, join, link, link up " ), in German law of composition or combination law is a rule of mathematics. A (two -digit ) operation is associative, if the order of execution does not matter. In other words: The bracketing more associative links is arbitrary. Therefore, one could also call " clip law" it vividly.
In addition to the associative law are distributive and commutative law of fundamental importance in mathematics.
Definition
In a sum or product term the addends or factors may be associated with any brackets. This is also true for more than three addends or factors.
A binary operation on a set is called associative, if for all the associative law
Applies.
Conclusions
In The associative law can introduce a simplified clip- free notation. because of
The term
Clear, since from any bracketing is always followed by the same result.
Examples
As links to the real numbers addition and multiplication are associative, it is, for example, addition:
Multiplication:
Subtraction and division, however, are not associative, because it is, for example, subtraction
Division:
The power is not associative, because, for example
Applies.
Classification
The associative law is one of the group axioms, but is already called for the weaker structure of a semigroup.