Ataxia telangiectasia
The Louis - Bar syndrome (also ataxia telangiectasia ( ataxia- telangiectasia ) or Boder - Sedgwick syndrome) is an inherited systemic disease and is counted among the phakomatoses and chromosome breakage syndromes. In the neurological system it is expected to Heredoataxien ( inherited ataxias ). Was named the disease after the Belgian doctor Denise Louis bar.
Epidemiology
The mode of inheritance is autosomal recessive, affecting the so-called AT gene on chromosome 11 q23 locus. The mutated gene is referred to as an ATM. 0.5 to 1 % of the healthy population (heterozygous ) carriers of the mutation. Approximately one out of 40,000 newborns homozygous for the defective gene and is developing the ataxia-telangiectasia.
Pathophysiology
The ATM gene encoding the serine protein kinase ATM, which plays a role as a sensor of DNA damage caused by UV radiation, and as a regulator of DNA repair processes or programmed cell death (apoptosis). From the fact that many cell lines are affected by the mutation, the variety of symptoms of the Louis-Bar syndrome explained.
Symptoms
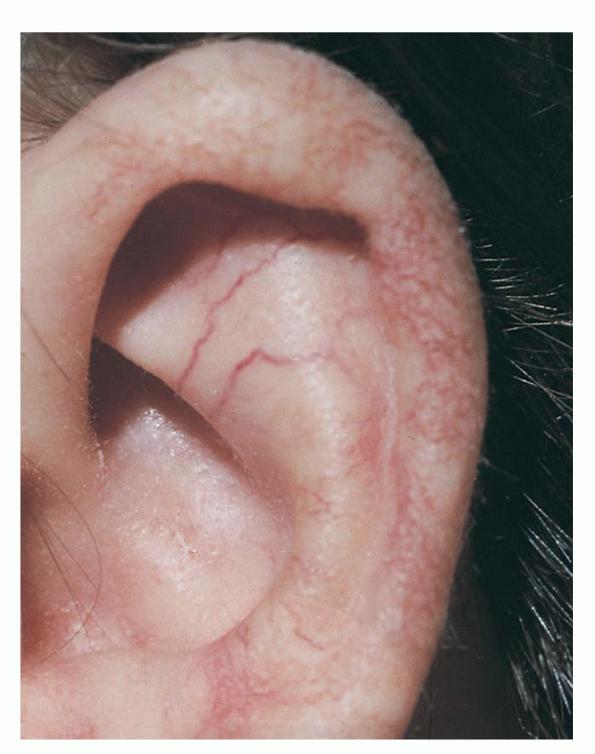
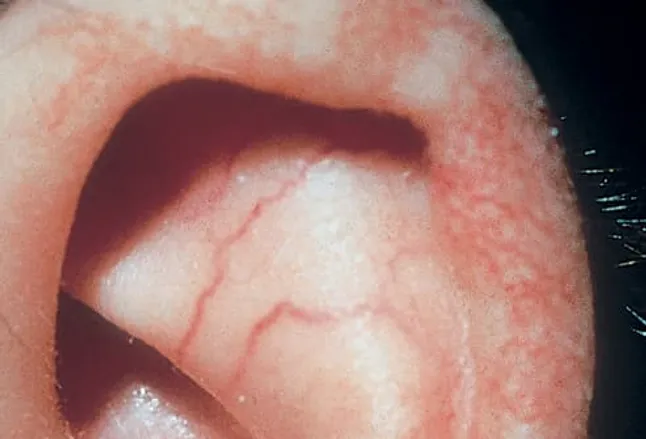
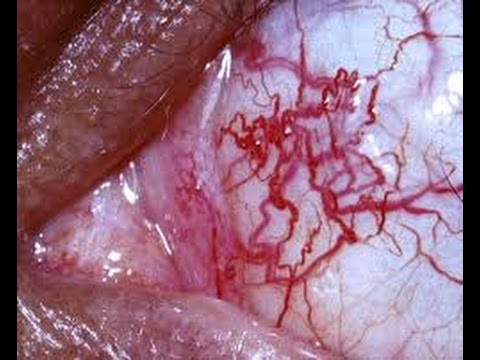
The first symptoms occur around the second or third year of life. It is characterized by a cerebellar ataxia (among active and inactive uncertainty) with cerebellar atrophy ( shrinkage substance ), especially in the area of the vermis, athetosis ( dystonic movement disorder ), disorders of eye movements as well as a physical and later psychological development is lagging behind. In addition, contact telangiectasia (extensions of the small arteries ) especially in the face and on the conjunctiva of the eye, and the affected children have a T- cell defect decreased immune competence, so they tend to infections and much more frequently than the normal population leukemias and Hodgkin 's lymphomas develop. The cancer rate is higher by a factor of 100 than in the general population. Diseased therefore have an increased sensitivity to ionizing radiation and should be X-rayed as little as possible. Other common symptoms include salivation ( drooling ) and hypogonadism (ripening disorder of the gonads ).
Diagnosis and treatment
The diagnosis is often already made clinically. Confirmation can be a proven by imaging cerebellar atrophy and reduced immunoglobulin levels and lymphopenia. Alpha -1 -fetoprotein levels are often elevated.
A causal treatment is not possible. It will be treated especially pulmonary infections with antibiotics. What is important is the consistent vaccination of children, with live vaccines are absolutely contraindicated.
Forecast
Life expectancy is significantly reduced due to recurrent pneumonia and increased cancer rates. In the literature, the median life expectancy is estimated at 20 years. There are known cases where people have far exceeded with this syndrome twentieth year, depending on the severity and course of the disease.
Swell
- Wallesch (eds): Neurology. Diagnosis and treatment in clinic and practice. Elsevier Urban & Fischer, 2005. ISBN 3-437-23390-4.
- Hereditary disease
- Disease in pediatrics
- Disease in neurology