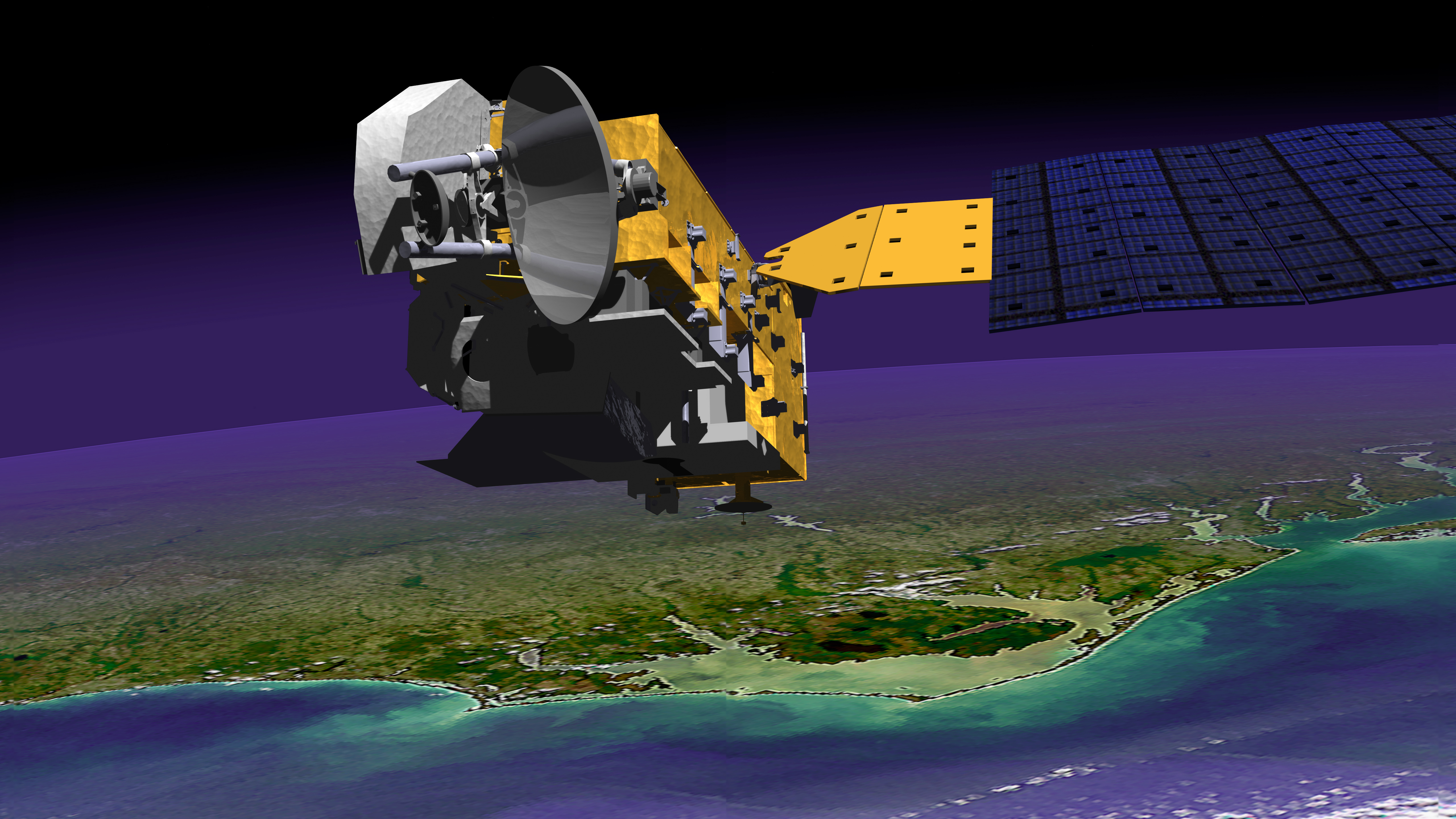
Aura (satellite)
Aura is the name of Earth observation satellites of the U.S. space agency NASA, which was launched on 15 July 2004 with a missile of type Delta 2. Aura is located in a sun-synchronous orbit with an inclination of 98.2 ° in about 700 km altitude. The five satellites Aura, Aqua, CloudSat, PARASOL and CALIPSO together form the A-Train.
Main objectives of the mission are the observation of the ozone layer, monitoring of air quality ( ground-level ozone, nitrogen dioxide, aerosols) and climate change. The satellite began after a calibration phase of the routine collection of data on 14 October 2004.
The satellite has four instruments on board:
- HIRDLS (High Resolution Dynamic Limb Sounder ) measures the infrared radiation by ozone, water vapor, chlorine fluorocarbons, methane and various nitrogen compounds.
- MLS (Microwave Limb Sounder ) measures the output of various trace gases microwave radiation.
- OMI ( Ozone Monitoring Instrument) operating in the visible and ultraviolet regions of the electromagnetic spectrum and provides high-resolution images of the global ozone distribution of other trace gases and aerosols.
- TES ( Tropospheric Emission Spectrometer) measures the concentration of ground-level ozone and other trace gases by their infrared emissions.