Backward-Diode
The Backward diode (reverse diode) is a special form of the tunnel diode. In spite of the English vocabulary is the preferred international term "back diode".
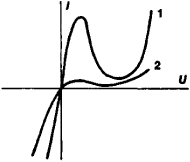
In comparison to the normal current characteristic of the tunnel diode bump was almost completely suppressed. Through this property, the backward diode has a wide range of about 0.5 V in the current-voltage characteristic in which it has a substantially constant current, which can be interpreted as the reverse current. Note that the characteristic image is rotated with respect to the normal representation in the tunnel diode 180 °.
The Backward diode is thus operated in the reverse direction, hence its name. The nearly flat characteristic up to a voltage range of about 0.5 V is used as a blocking area. Thereafter, the curve will return to the exponential profile of a normal diode. The backward diode having a low forward voltage ( low internal resistance ), and further the high speed of the original tunnel diode.
Its field was mainly the high frequency technology. It has been used herein as a rectifier, in the mixer circuit or envelope detectors in the case of small signal levels. Through the development of alternative active semiconductor components of the radio frequency technology, the importance of the backward diode has gone almost completely lost and it is therefore only difficult to obtain.