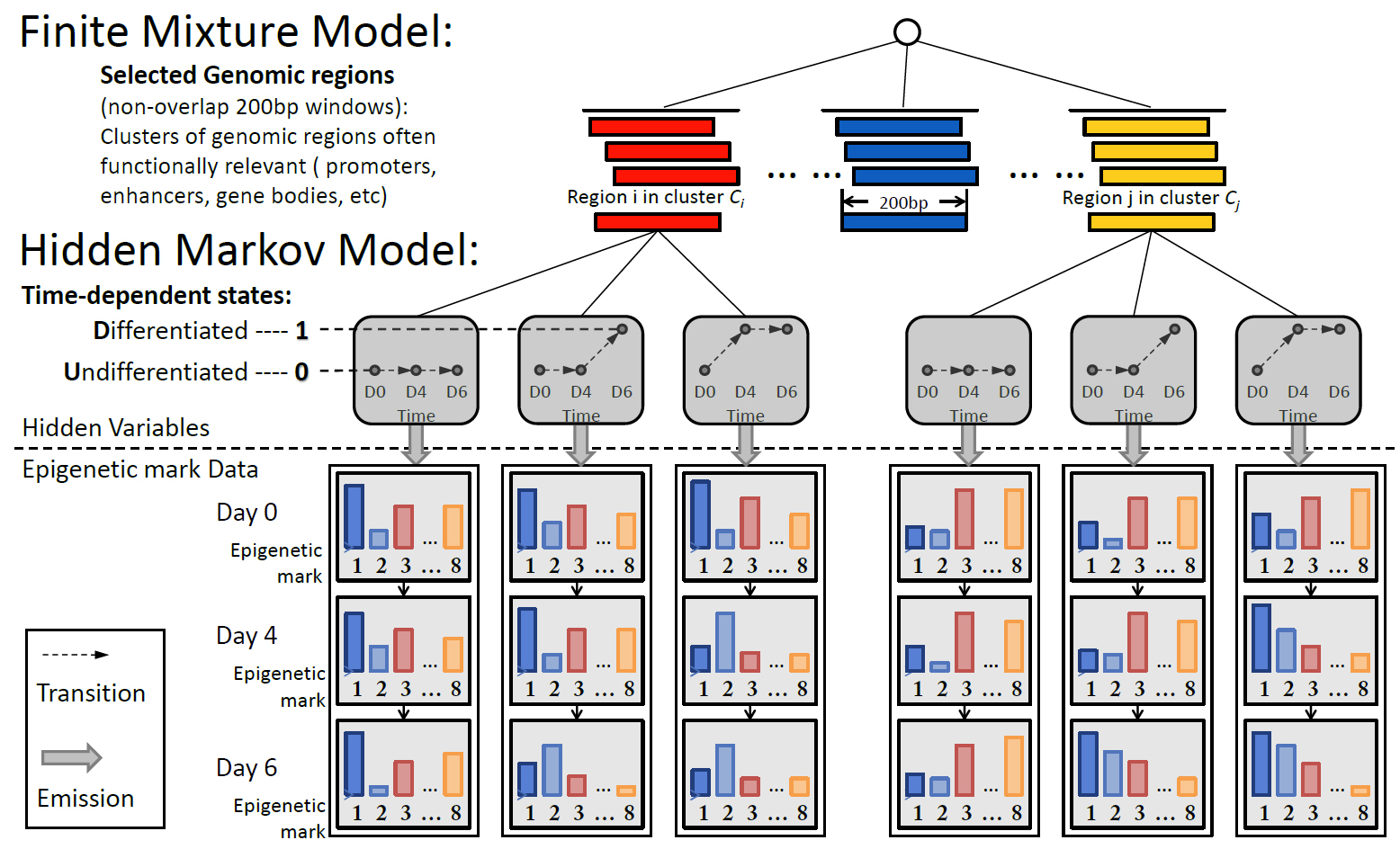
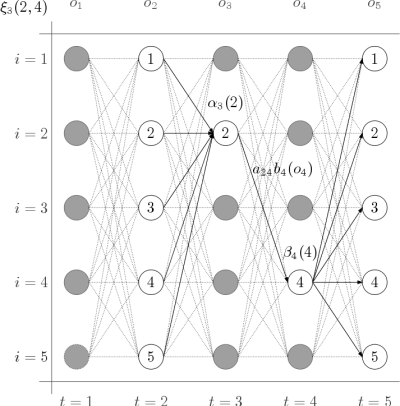
Baum–Welch algorithm
In computer science and statistical calculation models of the Baum-Welch algorithm is used to find the unknown parameters of a Hidden Markov Models ( HMM). It uses the forward-backward algorithm for calculating intermediate results, but is not identical thereto.
The Baum-Welch algorithm is an expectation -maximizing algorithm. Computing the maximum likelihood estimate ( maximum likelihood estimates ), and the so-called posterior fashion estimates for the given parameters ( transitional and emission probability ) of an HMM, when only the emissions are given as the training data.
The algorithm works in two steps: First, it calculates the forward probability (forward probability ) and the backward probability (backward probability ) for each state of the HMM. Secondly, on the basis of this first step, it calculates the frequency of the transition - emission pair values and dividing this by the probability of the entire string (so-called posterior decoding ). This leads to the calculation of the expected count of each transition emission pair. Every time a single transition is found, the value of the quotient of the transition and the probability of the entire string increases. This value can then be taken as the new value of the transition.
The Baum-Welch algorithm is an instance of the EM algorithm and was named after Leonard E. Tree and Lloyd R. Welch.