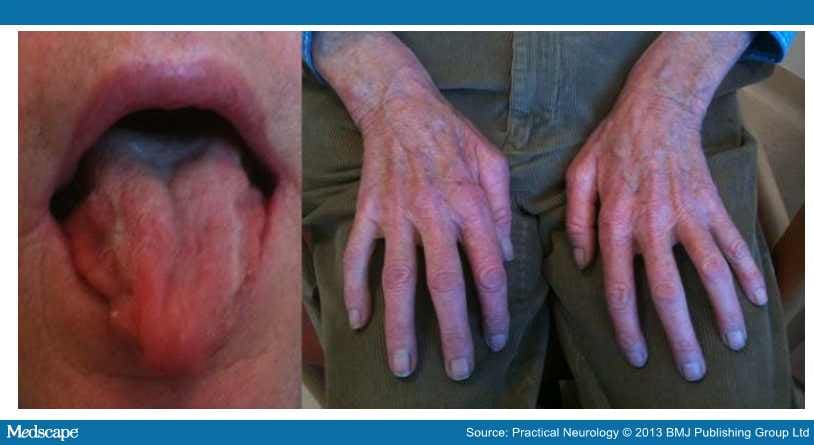
Benign fasciculation syndrome
The term benign fasciculation (abbreviated BNF ) refers to the occurrence of involuntary, in some cases, through the skin visible twitching of the muscles ( fasciculation ). The Anglo-Saxon literature uses the term benign fasciculation ( syndrome ) interchangeably. The BNF comes to no clinical significance per se.
The BNF is often found in healthy people, but may also result from a motor neuron disease ( MND ) may occur. Then there is an important differential diagnosis for example, for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis dar. Typically, the BNF is associated with neither atrophy nor weakness of Muskelatur, even with abnormal excitation processes in motor neurons ( MUP) and occurs only after exercise. There is evidence that spontaneous benign fasciculations may occur when a large part of the "healthy" population, especially in the muscles of the hands and feet. Thus, the BNF is ultimately a diagnosis of exclusion, without independent clinical significance.