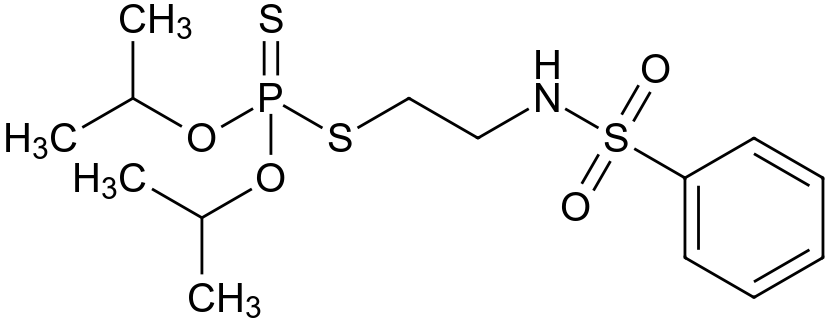
Bensulide
- O, O- diisopropyl S-(2 - phenylsulfonylaminoethyl ) phosphorodithioate
- Prefar
- N-(2 - ethylthio ) -benzenesulfonamide S- ( O, O- diisopropyldithiophosphat )
- Dithiophosphoric acid O, O -bis (1 -methylethyl) -S-( 2 - ( (phenylsulfonyl ) amino ) ethyl ) ester
Colorless solid
Fixed
1.25 g · cm -3
34.5 ° C
200 ° C ( decomposition)
- Practically insoluble in water (25 mg · l-1 at 22 ° C)
- Soluble in acetone, ethanol, 4-methyl pentan- 2-ol and xylene
Attention
271 mg · kg -1 ( LD50, rat, oral)
Template: Infobox chemical / molecular formula search available
Bensulide is a chemical compound selected from the group of the thiophosphoric acid esters and sulfonamides.
History
Bensulide was brought in 1964 in the United States for control of finger millet and one year of bluegrass on lawns by the Gowan Company on the market. 1968, was patented for controlling grasses in agriculture. About 250 tons are used each year in the United States.
Production and representation
Bensulide, by a multi-stage reaction of phenylsulfonyl chloride (to be contacted with ethanolamine, and the reaction of thionyl chloride ) and phosphorus (V ) sulphide (to be contacted with isopropanol and ammonium hydroxide ) are obtained.
Properties
Bensulide is a colorless solid which is virtually insoluble in water. It decomposes above a temperature of 200 ° C. The technical product is at a temperature of 34 ° C, a viscous amber liquid. Bensulide acting as cholinesterase inhibitors and thus has adverse effects on the central nervous system.
Use
Bensulide is used as a herbicide in a variety of fruits and vegetables. Trade names are Betamec, Betasan, Dishan, Exporsan, Prefar and pre- san.
In Germany, Austria and Switzerland, no pesticide is approved, which contains bensulide.