Benzoin condensation
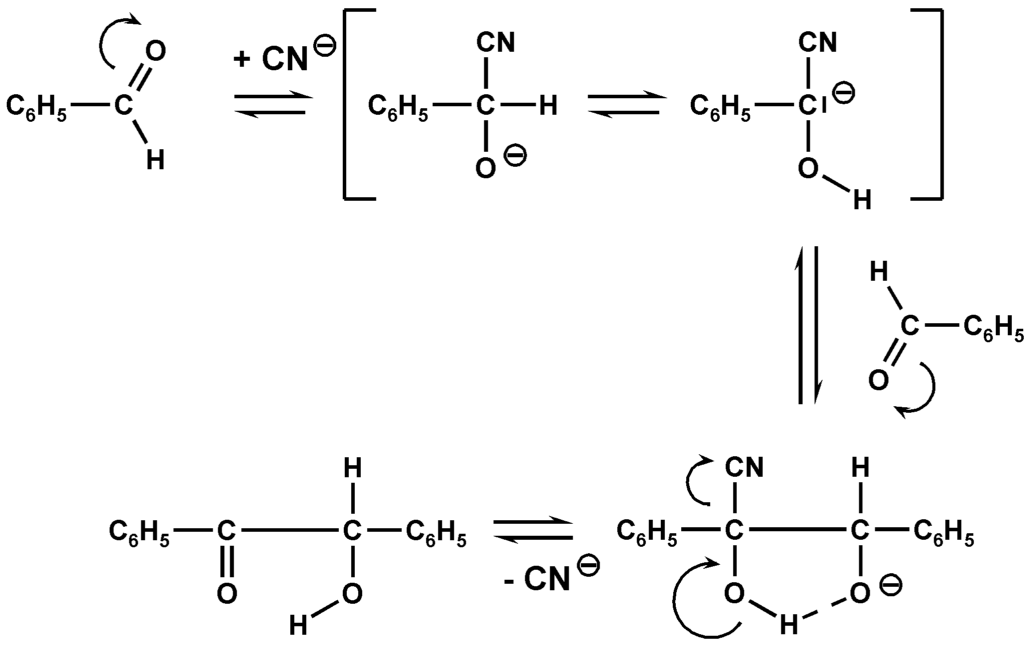
The benzoin addition ( frequently but erroneously referred to as benzoin condensation) is usually the addition of aromatic aldehydes, especially benzaldehyde under cyanide catalysis to aromatic α - hydroxy ketones ( benzoin ). The mechanism was proposed in 1903 by Arthur Lapworth. Shown is the reaction on the example of the reaction of two molecules of benzaldehyde to benzoin.
Mechanism
The mechanism of the reaction is also illustrated by the above example:
In a first step is carried out by the cyanide ion, a reversal of the Carbonylkohlenstoffes the benzaldehyde (1). By addition of cyanide ion to the carbonyl group, the anion of the corresponding cyanohydrin produced. For this the tautomeric carbanion 2 is formed by transfer of a proton from carbon to oxygen, which has been attacking nucleophilic another benzaldehyde. Under an intramolecular proton transfer and elimination of cyanide from molecule 3, the product of benzoin ( 4) is formed. The reaction is reversible. The cyanide is a very specific catalyst and, in the course of the reaction three tasks. First, it acts as a nucleophile, secondly, it facilitates its - I effect the spin-off of the proton and third, there is leaving group.
The two aldehyde molecules have different roles. The aldehyde to write its proton is referred to as a donor, the one that receives it as an acceptor. Some aldehydes can only act as donor ( eg, 4 -dimethylaminobenzaldehyde ), others can take over both roles (eg benzaldehyde ). This allows the selective synthesis of some unsymmetrical benzoin.
The reaction can be extended by the use of certain thiazolium salts in basic medium also to aliphatic aldehydes and mixtures of aliphatic and ( hetero) aromatic aldehydes. The mechanism is essentially similar to the above.
Obtained in these reactions, α -hydroxy ketones are also called acyloins and are important starting materials for further syntheses, particularly heterocyclic compounds.
The addition can be carried out (for example, methyl vinyl ketone ), and to α - β -unsaturated ketones. This variant is called the Stetter reaction.
In the organism occurring, there is responsible for the synthesis of acyloins Coenzyme Thiamine similarly contains such a thiazolium salt.