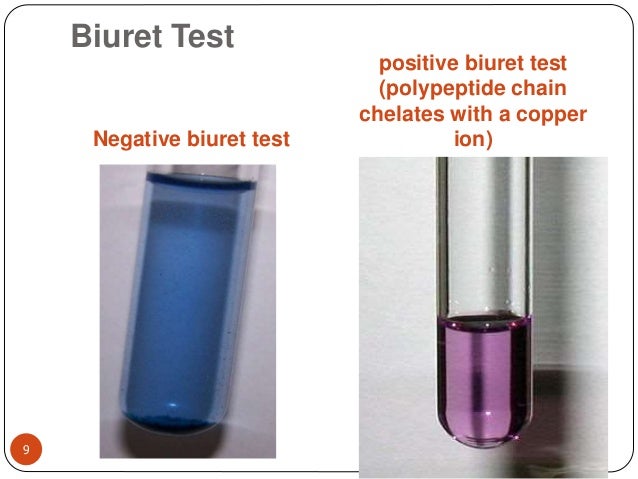
Biuret test
The biuret reaction, the biuret and biuret assay or test, is a chemical detection reaction of biuret and proteins (proteins), or more precisely for their peptide bonds.
Proof of principle
Peptide bonds are a fundamental component of proteins. With the biuret test proteins can be colorimetrically detected in samples.
This protein determination method, connections with at least two peptide bonds in aqueous alkaline solution a colored complex with divalent copper ions. This results in a color change to dark purple. This detection method is - compared to other staining methods - but one of the unspezifischsten. For example, also chelate copper ions and tyrosine residues contribute to the formation of dye at.
The detection limit is 1 to 10 micrograms of protein per milliliter.
In practice, the solution to be examined is treated with sodium hydroxide solution, little copper sulfate solution is added and shaken. The measurement of the color intensity can be carried out at 540 to 550 nm.
Despite the name, no need for the biuret reaction. Rather biuret forms because of its amide bond a similar complex and can therefore serve as a positive control.
Further detection reactions for proteins
- Xanthoproteic reaction
- Millon reaction
- Ninhydrin reaction
- Kaiser test
- Bradford assay
- Protein determination according to Lowry
- Folin- Ciocalteu reagent