Blood culture
A blood culture is a microbiological examination of the blood, in which an attempt is made pathogens (mostly bacteria) to multiply, which are located in the blood by cultivation, to measure them by and identified.
Indications ( situations in which the investigation is carried out )
- Septicemia ( " blood poisoning" )
- Unexplained fever
- Endocarditis ( endocarditis )
- Fever in immunosuppressed patients ( patients with HIV chemotherapy)
- Pneumonia ( lung infection )
- Meningitis ( meningitis )
Method
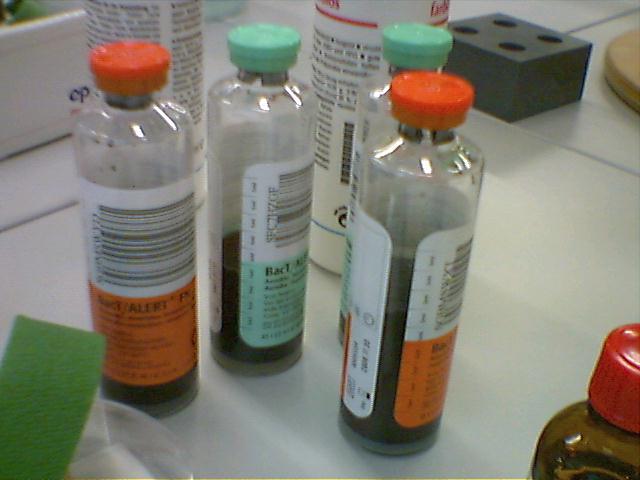
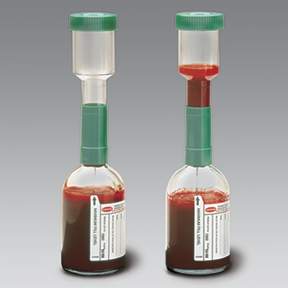
With the help of blood cultures to search for disease-causing bacteria. For this, the patient is taken a certain amount of blood, and immediately added to the " blood culture bottles ." There are also more modern retrieval systems where the blood is passed directly into the filled with a nutrient medium bottles. It must be working as usual in clinical microbiology, sterile and clean. The venous blood should - depending on the indication - are repeatedly recovered at a distance of at least half an hour from different places.
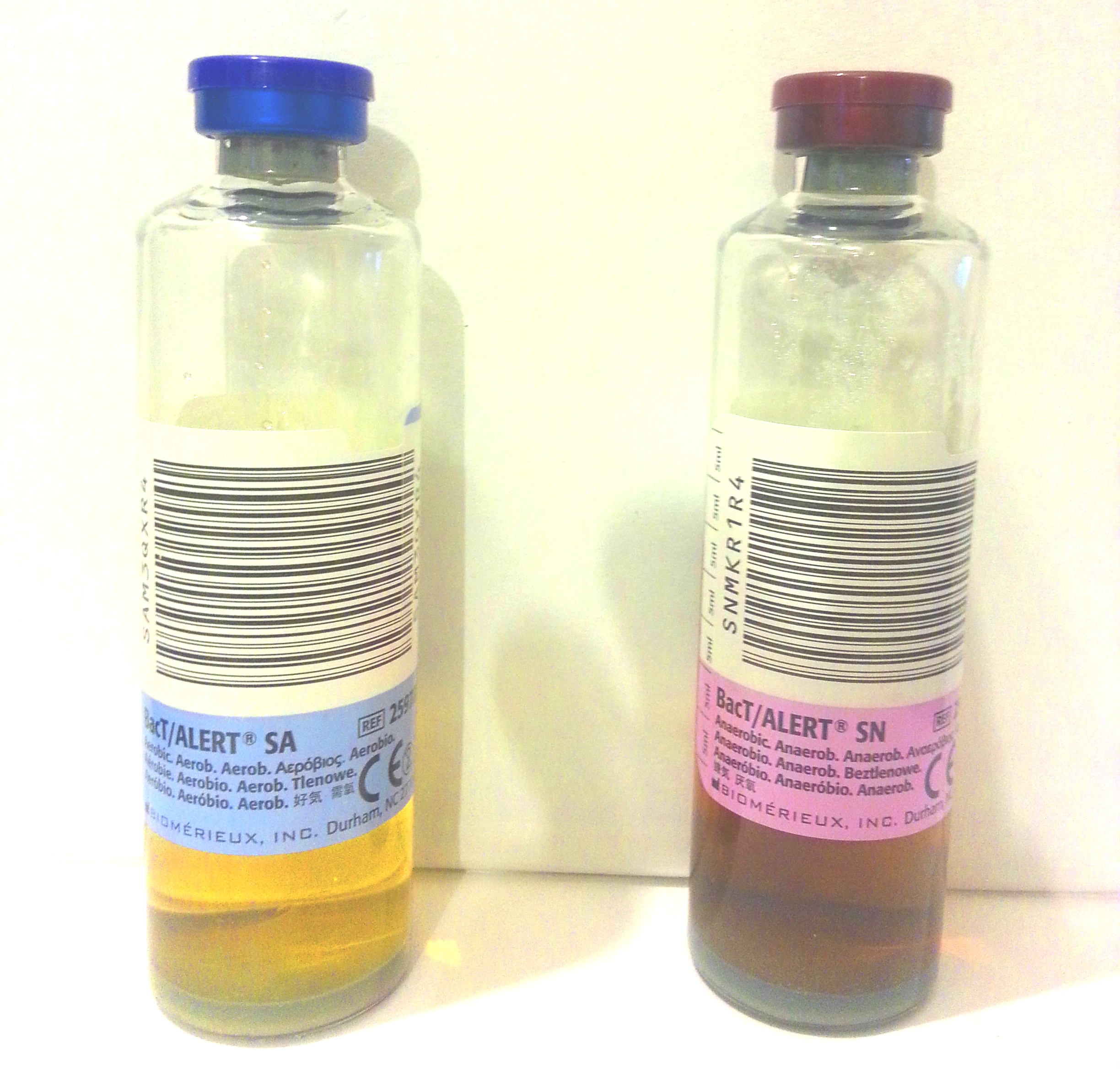
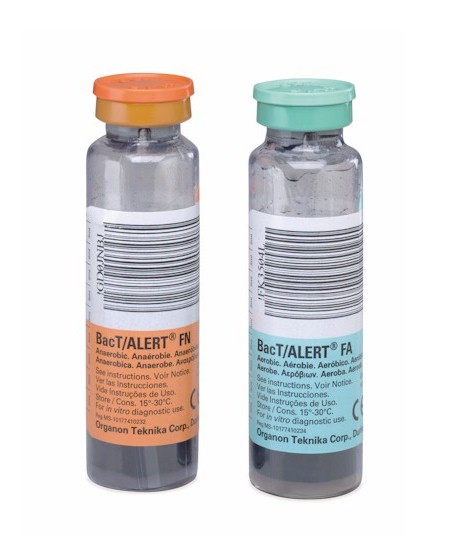
In these bottles is next to a so-called Bouillon, a gas mixture. The latter differs between the bottle for aerobic and anaerobic pathogens.
- Anaerobic bottle contains more carbon dioxide
- Aerobic bottle contains more oxygen
Aerobic and anaerobic bottle each provide favorable growth conditions for different types of bacteria (so-called aerobes and anaerobes ). For removal of blood cultures therefore always include the filling of two bottles, a so-called " pair of blood cultures ".
Processing
In the microbiology laboratory, the bottles are placed in the incubator and incubated at 37 ° C for several days.
It used to be daily checked with the naked eye whether opacities are visible in the liquid. In addition to the bottle wall a solid culture medium was applied, followed by bacterial or fungal colonies could settle.
Today, there are devices that pick up the lab technicians that work. The bottles are filled with a specific gas mixture. When this mixture is changed by the metabolism of bacteria, this can be measured for the very sensitive camera and he immediately gives an alarm. The lab can be as equal to conduct further investigations into the ways in which bacterial identification and susceptibility / resistance of the pathogen to certain antibiotics. Thus, a rapid diagnosis is possible and the patient can be treated accordingly.
Sources of error
- Asepsis: Wrong germ provisions for non- strict aseptic blood collection or insufficient skin disinfection. The culture result brings typical skin bacteria in this case.
- Death of susceptible pathogens: bacteria can die off to the lab in the culture bottle itself to transportation. This is V.A. with already ongoing antibiotic therapy.
- Not anzüchtbare or bacterial pathogens
- Bacteriology
- Laboratory Medicine