Blood urea nitrogen
Blood urea nitrogen (English blood urea nitrogen ), generally abbreviated BUN is a measure of the nitrogen content of the metabolic end product of urea in the blood. It is expressed in mmol / l ( SI unit ) or in mg / dl (deprecated) specified. Since each urea molecule ( molar mass 60.06 g) two nitrogen atoms ( molar mass of 28.01 g), the concentration of the nitrogen content ( BUN " ) can be calculated easily from the concentration of urea by the urea concentration multiplied by 0.467.
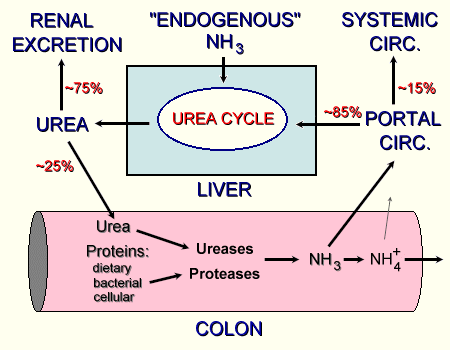
The liver produces urea in the urea cycle as a waste product of protein digestion. Normal human blood serum should contain 7-25 mg of urea nitrogen per 100 ml. Individual laboratories can specify different limits due to different test procedures, however.
The BUN is one of the renal retention parameters and is used primarily as a medical indicator in nephrology. The determination of BUN is often performed in the Anglo- American sphere, while, for example in Germany instead, the urea concentration is determined.
Unit
The conversion from mg / dL to mmol / L by multiplying by 0.357.
References and Notes
- Medical laboratory investigation procedure
- The diagnostic method in Nephrology