Body plethysmography
Bodyplethysmography ( often called whole body plethysmography, or large lung function ) is a pulmonology procedure for measuring pulmonary and respiratory parameters. A variety of measured in the body plethysmography respiratory physiological variables - like the breathing resistance, the residual volume or total lung capacity - is with other measurement techniques, such as spirometry, are not accessible.
Introduction
The method used today is the Bodyplethysmography goes back to the introduction of the method by DuBois in 1956. In the clinical area and in practices established pulmonologists Bodyplethysmography is considered diagnostic method of choice. The investigation by a body plethysmograph is the ideal lung function test method since it can calculate the specific airway resistance including breathing loop, the thoracic gas volume and all parameters can be derived from the same investigation on the transition measures of spirometry addition. Employees dependence of this method is less than with spirometry and the time overhead is low. The high cost of equipment and the high cost, however, explain why a body plethysmograph are practically found only in hospitals and specialists.
Principle of measurement
Determination of breathing resistance
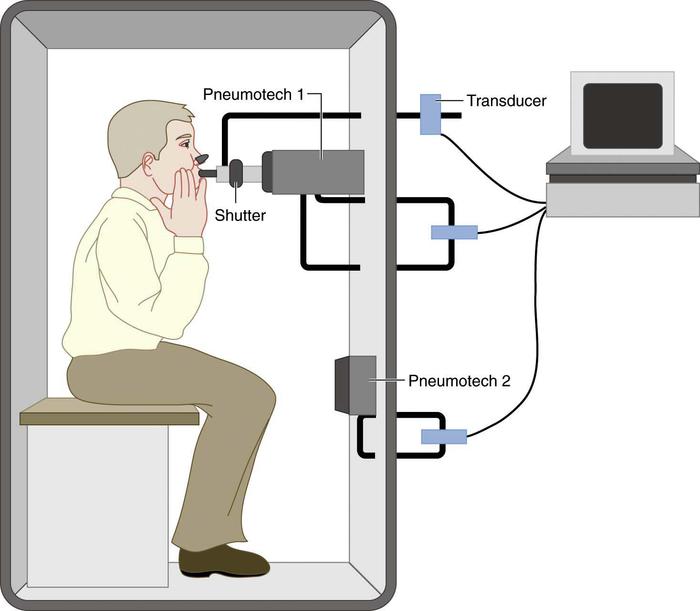
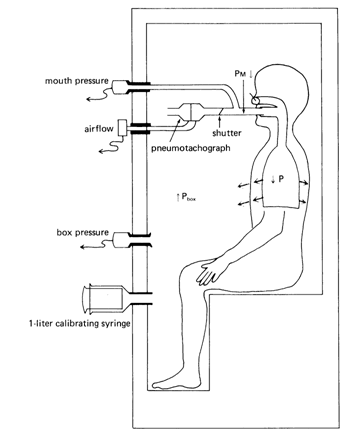
The Bodyplethysmograph runs as a cabin with a (largely) closed volume of air, it looks like a small phone booth. The cabin has a minimum leakage at a cabin pressure increase by the body heat of the patient to compensate. During the examination, the patient breathes in order to determine flow characteristics through a spirometer. For inspiration now raises the patient's chest, which the volume of air in the cabin minimally reduced, thus increasing the pressure. In tidal breathing can be seen now that the pressure change is needed to produce a certain flow. The analysis of these so-called breathing loop allows conclusions on the compliance of the lungs and can thus easily and quickly uncover diseases such as a simple obstruction ( shallower breathing loop ) or COPD ( triangular protuberance in the expiratory part of the breathing loop). The specific airway resistance Sraw then corresponds to the slope of the breathing loop. For the determination of the total airway resistance is still the thoracic gas volume (TGV) needed: which is determined in the next step.
Determination of thoracic gas volume
The measurement of the thoracic (often: intrathoracic ) gas volume based on the physical law of Boyle and Mariotte, after at constant temperature, the product of pressure and volume remains constant. As described, it is due to the respiratory movements, respectively in a compression or expansion of the trapped gas volume within the thorax. While in the inhaled rest position, ie at the end of exhalation, the air pressure in the lungs corresponds to the external pressure increases with inspiration by the lifting of the rib cage, the volume of the lungs, which in turn drops the pressure. Therefore, the law of Boyle and Mariotte here are applied as follows:
The pressure here corresponds to the normal outside pressure at rest. The volume change can be determined by the change of the cabin pressure during inhalation. The change in the pressure is determined by a pressure gauge at the mouthpiece of the patient. A shutter closes briefly the mouthpiece, so for a brief moment, no more breath flow can be measured and thus no pressure drop across the airway resistance exists. The measured pressure corresponds solely to the pressure in the pulmonary alveoli, the intrapulmonary pressure. Thus, the above equation for the unknown lung volume, which corresponds to the thoracic gas volume, to be changed:
With other parameters determined by simple spirometry can now also be closed to the total lung capacity and residual volume the.
Although the physics of this method does not appear overly complex, this technique mastered by only a few manufacturers. Worldwide only offer about a dozen companies a body plethysmograph. This is partly due to the extremely small pressure differences that occur during inspiration, but also to the great disturbances, such as cabin heating, phase shift of the pressure or vulnerability to external pressure influences the sensitive sensors.
Indication
Spirometry provides the first evidence for the presence of lung disease, and is suitable for the observation of the disease and treatment course. For a definitive diagnosis, a body plethysmography is however unavoidable. Apart from the basic distinction between eg Asthma and COPD, allows Bodyplethysmograph rapid classification of the obstruction in eg homogeneous obstruction, COPD or extrathoracic stenosis. Also for safe diagnosis of restrictions, pulmonary emphysema or pulmonary fibrosis requires a body plethysmography.