Boord olefin synthesis
Boord the olefin synthesis, or is a name Boord elimination reaction of the organic chemistry. The first report of it dates from the year 1930 by Cecil E. Boord. This reaction has a variety of applications in the production of alkenes.
Mechanism
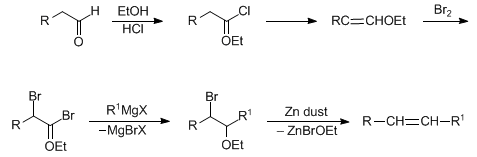
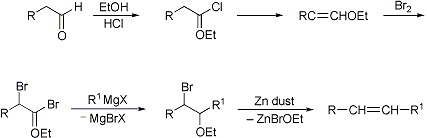
The figure shows a postulated mechanism. The reaction is characterized by a wide range of applications as well as high yields.
An aldehyde 1 is protonated with hydrogen chloride to give 2. With ethanol, a protonated hemiacetal forms 3 and 4 by nucleophilic attack of a chloride ion and elimination of water produced unstable chlorinated ethers 5, is cleaved from the hydrogen chloride to give 6. The halogenation of 6 (shown here by way of example with bromine ) provides, over that a bromonium ion 7 to the double- brominated ether 8 latter react with a Grignard reagent to said α - brominated ether 9 simply by the addition of zinc is formed of 9 via intermediate 10, by eliminating the alkene 11 as an (E, Z)- mixture. Zinc may also be replaced by magnesium or sodium. With the use of zinc usually an E1cb mechanism is postulated.
The reaction speed of the reaction can be controlled by the length of the alkyl group of the added alcohol. The larger this group, the slower the reaction.