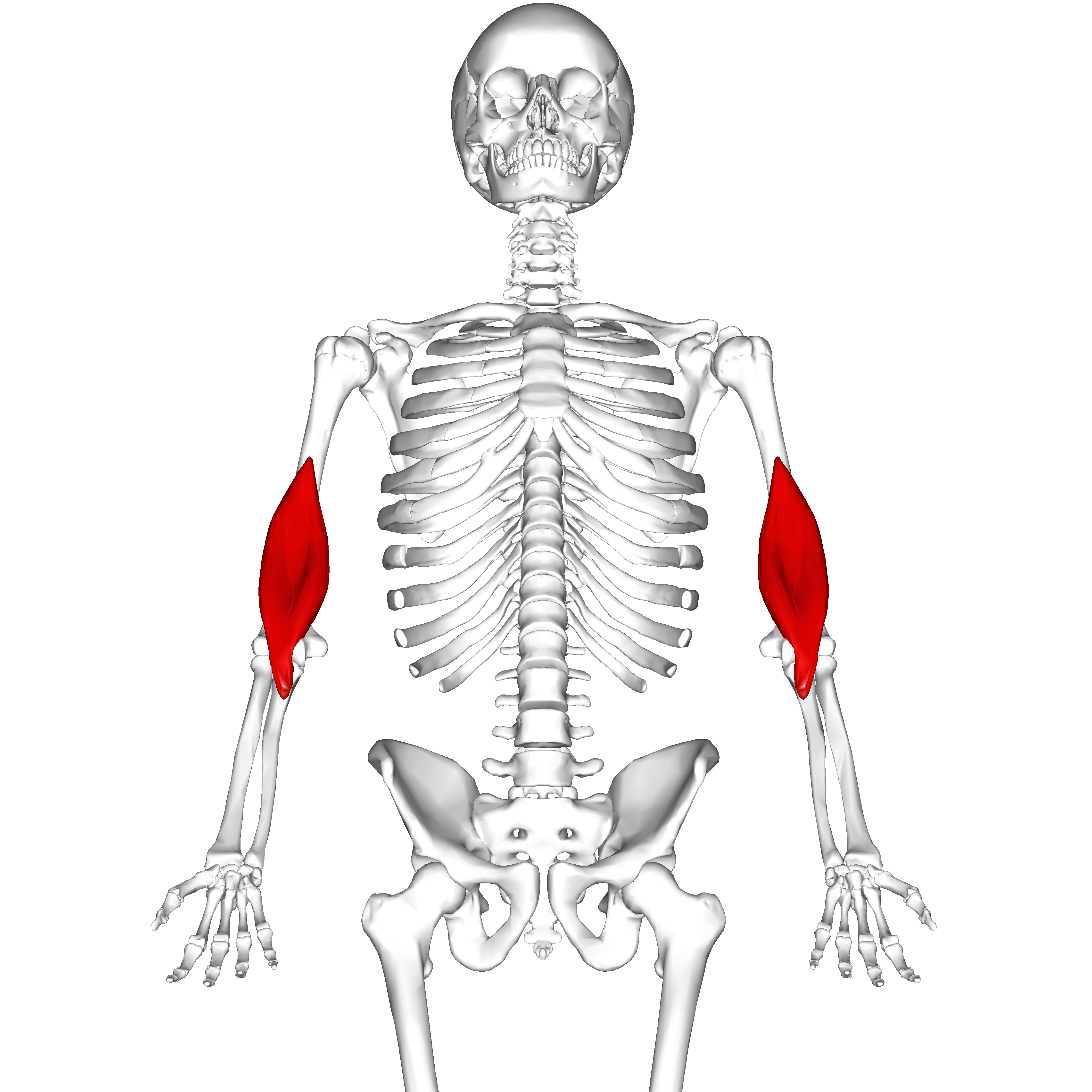
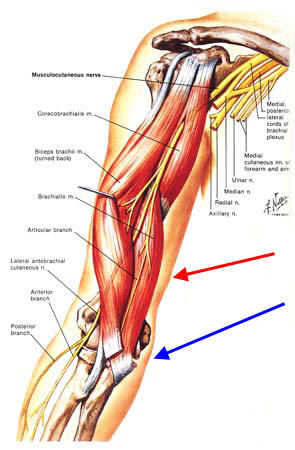
Brachialis muscle
The brachial muscle (Latin for " upper arm muscle ") is a skeletal muscle and is located behind the biceps brachii muscle on the outside of the upper arm. Its upper third is covered by the deltoid muscle.
Function
The brachial muscle pulls, like the biceps, the forearm is facing up, bends the arm at the elbow (flexion ), especially in the forearm pronated (palm down ). In contrast to the biceps brachialis muscle flexes the forearm in both pronation and supination in because it tackles the ulna. He is even stronger than the biceps brachii. This is not only on the mass and the larger physiological cross-section of the muscle, but also the fact that he only has one joint, the elbow joint, pulling away and not like the biceps brachii also over the shoulder joint. Thus he may delegate his power better. If a heavy load is to lift the M. brachialis does most of the work and initiates flexion when the arm is fully extended.
Antagonist is the triceps brachii of the same arm.
Varieties
Normally, the M. brachialis is on the outer, weaker forearm bones, the ulna. Occasionally, it is also grown but on the spoke. However, this variety in approach leads to no difference in the load, because the radius and ulna are through fixed fibers ( interosseous membrane ) connected to each other and keep all the loads together.